The Hazards of Maintaining a Septic System for homeowners DIY
 |
| Maintaining a Septic System |
Introduction
Subsection 1: Health Risks
Maintaining a septic system can expose you to health hazards including infectious diseases hazardous gases and electrical shock. Sewage carries harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause infection and illness, especially in people with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, children, and the elderly.
Exposure to hazardous gases is one of the risks involved in working with a septic system. Decomposing waste in the tank produces hazardous gases that can displace oxygen, creating an environment with little oxygen to breathe. Methane gas produced in the septic tank is also explosive, which can be a significant hazard if not adequately ventilated.
Electrical shock is another risk involved in working with a septic system. Pump chambers contain electrical wiring, and extra caution should be taken when working around them. Avoid using electrical devices that may come into contact with sewage and never smoke or light a flame near a septic tank.
To minimize exposure risks, homeowners should always assume that sewage is hazardous and can easily spread infectious disease. Remember to use the buddy system, keep children, spectators, and pets away from the septic system, and never leave open septic tanks unattended.
Subsection 2: Safe Work Practices
When working with a septic system, it's important to follow safe work practices to minimize exposure risks. The buddy system should always be in place, and homeowners should avoid working alone. Keep children, pets, and spectators away from the septic system while work is being done, and open septic tanks should never be left unattended.
If you're working around a septic tank, avoid entering or sticking your head into the tank to prevent exposure to hazardous gases. The work area should be ventilated, and electrical devices used with caution. Tools should be used to reach components, lift up floats or screens, and take measurements.
Furthermore, homeowners should be cautious of buried electrical lines and cables, telephone lines, satellite television or internet cables, and water lines. Call for a locate to avoid damaging these lines. Older septic tanks may have rusty, rotten, or broken lids that could break or collapse, so use caution when locating and digging.
 |
| Keep away from septic tank cleaning |
Subsection 3: Proper Hygiene
Proper hygiene is essential to prevent exposure to infectious diseases. Always cover or tie hair back, avoid eating, drinking, or smoking while working on the septic system, and wash your hands thoroughly with soap after the inspection is completed. Avoid touching your face and keep your hands below your shoulders to prevent sewage from dripping on your head. Cover open cuts or wounds, and maintain current immunizations.
It's also essential to avoid scratching exposed skin with dirty gloves or hands and to wash work clothes separately from regular laundry. If clothing is heavily soiled, rinse the clothes off first with a garden hose before laundering.
Subsection 4: Protective Clothing and Equipment
Protective clothing and equipment are necessary when working with a septic system. Safety goggles or glasses with side splash protection, dust masks that fit over the nose and mouth, disposable rubber gloves, work clothes, and boots should be worn to minimize exposure to hazardous materials.
Work clothes should be dedicated to septic system work, such as coveralls or rain gear. If using old clothing, make sure it can be discarded afterward. Avoid wearing loose clothing, jewelry, or anything that could get caught in moving parts.
Subsection 5: Clean-Up
After completing work on a septic system, it's important to properly clean up and sanitize the work area to prevent cross-contamination. Homeowners should use hoses properly to avoid backflow into the drinking water system and minimize splashing, spraying, and aerosolization of sewage.
Tools and equipment that come into contact with liquids or solids from the septic system must be cleaned and sanitized in a designated decontamination zone, preferably within the work area to minimize off-site contamination. If tools and equipment must be decontaminated off-site, they should be transported in an appropriate container used only for this purpose. Infectious diseases can be contracted and spread through the handling of contaminated tools and equipment.
- Electronic tools should be cleaned according to the manufacturer's instructions, and other tools and equipment should be decontaminated following a four-step process:
- Rinse off gross contamination with a dedicated garden hose using a stiff brush to remove dried material;
- Wash completely with soap and water, and let soak if needed;
- Rinse off the soap with a dedicated garden hose; and
- Sanitize all surfaces with a 20% bleach solution or other appropriate disinfectant, making sure to apply the sanitizer for a sufficient amount of time to kill pathogens.
Protective equipment and clothing should be removed upon leaving the work area to prevent tracking sewage into the home or vehicle. Isolate contaminated equipment and clothing in a plastic bag or other appropriate container for storage, washing, decontamination, or disposal. Wash your hands immediately or as soon as possible after removing gloves or other protective equipment or clothing.
 |
| septic tank cleaning hazards |
Subsection 6: Hiring a Licensed Professional
While homeowners can perform routine maintenance on their septic systems, they should be aware of their limitations and the potential risks involved. If at any time they are concerned about their ability to safely inspect or maintain their septic system, they should stop what they are doing and hire a licensed professional to perform the work.
Homeowners can contact their local health jurisdiction for a list of licensed professionals working in their area. Licensed professionals have the training and experience to safely maintain septic systems, minimizing the risks of exposure to hazardous materials.
Alternatively, you could get in touch and use a local septic tank service ( check local google listings) which will be aware of any possible situations impacting septic tanks in your location.
.png) |
| Septic Tank Services |
Subsection 7: Environmental Risks
Maintaining a septic system not only affects the health and safety of individuals but also the environment. Poorly maintained septic systems can lead to groundwater contamination, which can be harmful to the environment and potentially impact the surrounding community's water supply.
Over time, a septic system's soil absorption area can become clogged, resulting in untreated sewage backing up into the house or surfacing in the yard. This can cause environmental damage, unpleasant odors, and an increased risk of disease transmission. Additionally, improperly located or maintained septic systems can lead to the contamination of nearby wells and other water sources.
Homeowners should have their septic systems inspected regularly to identify potential problems early and take the necessary steps to avoid environmental contamination. It's also essential to properly maintain the system including regular pumping of the tank, to prevent backups and system failures.
In summary homeowners should be aware of the environmental risks associated with poorly maintained septic systems and take the necessary steps to protect their homes and the environment. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial to prevent contamination and ensure the proper functioning of the system.
Subsection 8: Understanding Your System
Understanding how your septic system works is essential to maintaining it properly. Homeowners should familiarize themselves with the system's location, components, and maintenance needs.
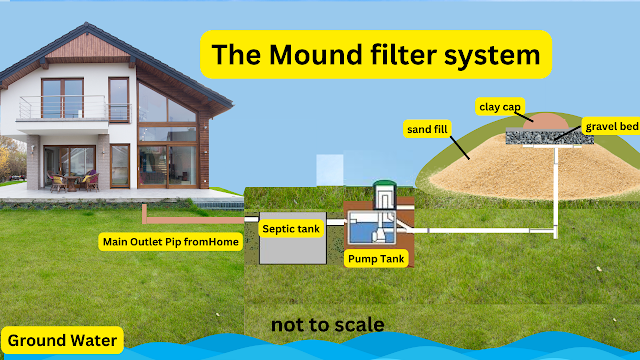
The septic tank is the primary component of the system and is responsible for separating solids from wastewater. Over time, the solids settle to the bottom of the tank and form sludge, while the liquid wastewater exits the tank and enters the drain field. Homeowners should have their septic tank pumped every 3-5 years, depending on the system's size and usage, to prevent the buildup of sludge and ensure proper functioning.
In addition to the tank, the drain field plays a crucial role in the septic system. It's essential to avoid driving or parking vehicles on the drain field, as this can compact the soil and reduce the system's effectiveness. Homeowners should also avoid planting trees or shrubs near the drain field, as the roots can damage the pipes and disrupt the system's functioning.
Subsection 9: Emergency response planning
In the event of a septic system emergency, homeowners should be prepared to take immediate action to protect themselves and their property. Signs of a system failure include slow drains, gurgling sounds, unpleasant odors, and wet spots or standing water in the yard.
If a septic system emergency occurs, homeowners should shut off the water supply to the house and avoid using any water until the issue is resolved. They should contact a licensed professional as soon as possible to assess the situation and take the necessary steps to repair the system.
Subsection 10: Local Regulations
Local regulations regarding septic systems can vary, and homeowners should be aware of the rules and regulations in their area. Some jurisdictions require regular inspections and maintenance of septic systems, while others have specific requirements for the installation and maintenance of the system.
Homeowners should contact their local health department or environmental agency for information on the regulations in their area. Understanding and following these regulations can help ensure the proper functioning of the septic system, minimize the risk of environmental contamination, and avoid potential fines or penalties.
Preventing Septic System Overload: Tips for Homeowners
The importance of maintaining a septic system cannot be overstated, and one crucial aspect of that maintenance is preventing septic system overload.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll discuss practical tips for avoiding overload and ensuring that your septic system remains in top shape.
Understanding Septic System Overload
First, it's essential to understand what septic system overload means.
Overload occurs when the septic system is overwhelmed by the volume of wastewater or solids, leading to inefficient functioning or, in worst-case scenarios, system failures.
By taking the appropriate measures to prevent overload, homeowners can extend the life of their septic systems and minimize the risk of costly repairs.
Water Conservation: A Key to Preventing Overload
One of the most effective ways to prevent septic system overload is by conserving water.
Reducing water usage not only eases the burden on the septic system but also benefits the environment.
Here are some practical water conservation tips for homeowners:
Install low-flow toilets and faucets to reduce water usage.
Fix leaks promptly to prevent excess water from entering the septic system.
Use a high-efficiency washing machine and run only full loads of laundry.
Space out laundry loads throughout the week instead of washing multiple loads in one day.
Limit shower times and avoid using high-volume showerheads.
Garbage Disposal On Septic System
Avoiding Garbage Disposals: A Common Overload Culprit
Using a garbage disposal can significantly contribute to septic system overload.Garbage disposals grind food scraps into small particles, which then enter the septic tank.
These particles increase the amount of solids in the tank, leading to faster sludge accumulation and a higher risk of overload.
To prevent this issue, consider the following tips:
Scrape food scraps into a compost bin or trash can instead of using a garbage disposal.If a garbage disposal is necessary, use it sparingly and avoid grinding fibrous or starchy materials, such as potato peels and celery.
Regularly pump the septic tank to remove accumulated solids and reduce the risk of overload.
Limiting Water Usage During Peak Times
Another essential tip for preventing septic system overload is to limit water usage during peak times.Peak times often include mornings when family members are getting ready for the day and evenings when they return home.
By staggering water usage, homeowners can avoid putting too much stress on their septic system at once.
Some ways to manage water usage during peak times include:
Staggering shower times among family members.Running the dishwasher or washing machine at off-peak hours.
Avoiding simultaneous use of water-intensive appliances, such as washing machines and showers.
Regular Maintenance: The Foundation of a Healthy Septic System
Regular septic system maintenance is crucial for preventing overload and ensuring the system's overall health.This includes:
Inspecting the septic system annually to identify potential issues.Pumping the septic tank every 3-5 years, depending on usage and tank size.
Keeping accurate records of septic system maintenance and repairs.
Monitoring the drain field for signs of overload, such as standing water or unpleasant odors.
Educating Household Members on Septic System Care
Finally, educating all household members on proper septic systemcare is vital for preventing overload.
This includes discussing the importance of water conservation, avoiding the use of garbage disposals, and limiting water usage during peak times.
By ensuring that everyone in the household understands and follows these guidelines, homeowners can minimize the risk of septic system overload and maintain a healthy, efficient system.
In conclusion
Maintaining a septic system is essential for the health and safety of your family and the environment. Homeowners should be aware of the potential risks involved in maintaining a septic system and take the necessary steps to minimize those risks.Regular inspections and maintenance of the septic system are crucial to identifying potential problems early and avoiding system failures. Homeowners should familiarize themselves with the system's location, components, and maintenance needs, including regular pumping of the septic tank.
Proper hygiene and the use of protective clothing and equipment are essential when working with a septic system to minimize the risk of exposure to harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
In the event of a septic system emergency, homeowners should be prepared to take immediate action to protect themselves and their property. Shutting off the water supply to the house and avoiding the use of any water until the issue is resolved can prevent further damage to the system and the property.
It's also important to understand and follow local regulations regarding septic systems. Contacting the local health department or environmental agency for information on the rules and regulations in the area can help ensure compliance and avoid potential fines or penalties.
By taking these steps, homeowners can maintain their septic system properly, protect their health and property, and avoid costly system failures and repairs. A well-maintained septic system not only benefits the homeowner but also helps protect the environment by minimizing the risk of groundwater contamination.
In summary, maintaining a septic system requires a combination of regular inspections and maintenance, proper hygiene, protective clothing and equipment, emergency preparedness, and adherence to local regulations. Homeowners who follow these guidelines can enjoy the benefits of a properly functioning septic system while protecting their health, property, and the environment.

.png)




.png)



Comments
Post a Comment