Ascending the Mound: A Comprehensive Guide to Mound Septic Systems
 |
| Mound Septic Systems |
Ascending the Mound: A Comprehensive Guide to Mound Septic Systems
Introduction
In areas where the traditional septic systems may not be suitable, alternative solutions like mound septic systems come to the rescue. These innovative systems offer both environmental and practical benefits, making them an excellent choice for homeowners in specific situations. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the ins and outs of mound septic systems, including their unique features, advantages, maintenance requirements, and frequently asked questions.
Mound Septic Systems Inspection Expenses: Wisdom from Seasoned Professionals
Boasting a collective experience spanning more than 40 years, my partner Jeane and I have navigated countless challenges and situations in the realm of septic systems. As experts in this field, we are enthusiastic about sharing the priceless insights we have acquired over the years with existing septic system owners and those considering new installations. This blog is devoted to offering valuable advice and direction on the expenses associated with mound septic system inspections and other relevant subjects.
1. What is a Mound Septic System?
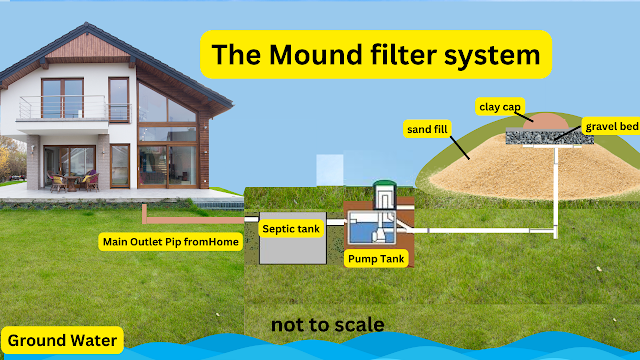
A mound septic system is an alternative to traditional septic systems, designed to overcome the challenges of dealing with shallow soil depths, high water tables, or bedrock close to the surface. These systems are engineered to treat wastewater by raising the drain field above the natural ground level, creating a "mound" to facilitate proper filtration and absorption of effluent.
2. Key Components of a Mound Septic System
The main components of a mound septic system include:
2.1 Septic Tank
The septic tank is the first stop for wastewater from the home. It is responsible for holding and separating solid waste from liquid waste, allowing the latter to flow into the next stage of the system.
2.2 Dosing Chamber
The dosing chamber receives the liquid effluent from the septic tank and distributes it evenly to the mound through a network of pipes, ensuring consistent and effective treatment.
2.3 Mound
The mound is an engineered structure made up of layers of sand, gravel, and topsoil, with a network of pipes embedded within it. The mound facilitates the filtration and absorption of effluent, allowing it to be safely returned to the environment.
3. Advantages of Mound Septic Systems
Some of the key benefits of mound septic systems include:
3.1 Versatility
Mound septic systems are adaptable to a variety of site conditions, including those with shallow soil depth, high water tables, or bedrock near the surface.
3.2 Environmentally Friendly
By raising the drain field above ground level, mound septic systems reduce the risk of groundwater contamination, protecting both the environment and public health.
3.3 Customization
Mound systems can be designed to accommodate the specific needs of a property, taking into account factors such as soil type, topography, and local regulations.
4. Maintenance Tips for Mound Septic Systems
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of your mound septic system. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
4.1 Regular Inspections
Schedule professional inspections of your mound septic system at least once every three years to ensure its components are functioning correctly.
4.2 Pumping the Septic Tank
Have your septic tank pumped every 3 to 5 years to remove accumulated solids and prevent system overload.
4.3 Monitoring Water Usage
Be mindful of your water usage to prevent overloading the system. Repair leaks promptly and consider using water-saving appliances.
4.4 Protecting the Mound
Avoid driving or parking vehicles on the mound, and refrain from planting trees or deep-rooted plants near the system to prevent damage.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
5.1 How much does a mound septic system cost?
The cost of installing a mound septic system can vary depending on factors such as location, soil conditions, and system size. Generally, mound systems are more expensive than conventional systems, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $20,000 or more.
5.2 Can I install a mound septic system myself?
Installing a mound septic system is a complex process that requires expertise in engineering, excavation, and plumbing. It's highly recommended to work with a professional septic system contractor who is familiar with local regulations and has experience with mound systems.
5.3 How long does a mound septic system last?
With proper installation and regular maintenance, a mound septic system can last anywhere from 20 to 40 years. Factors such as usage, soil conditions, and the quality of the system components can impact its lifespan.
5.4 Can a mound septic system be converted to a conventional system?
In some cases, it may be possible to convert a mound septic system to a conventional system. However, this will depend on the specific site conditions and local regulations. Consulting with a professional septic system contractor can help determine if this is a viable option for your property.
Disadvantages of Mound Septic Systems
Mound septic systems are an excellent solution for properties with challenging site conditions. However, they also come with some disadvantages worth considering. One major drawback is the higher installation cost compared to conventional systems, mainly due to the additional engineering and materials required. Additionally, mound systems require a larger space for installation, which can be a limitation on smaller properties.
Aesthetic concerns are another factor to consider. The visible mound can be an eyesore for some homeowners and may require landscaping efforts to blend it with the surroundings. Finally, mound systems can be more susceptible to erosion and damage from heavy rain or snow, requiring ongoing maintenance and monitoring to keep them functioning effectively.
Permits and Regulations
Before installing a mound septic system, it's crucial to ensure compliance with local permits and regulations. Each municipality has specific rules and guidelines governing septic system installations, including mound systems. Homeowners should consult with their local health department or permitting agency to determine the necessary permits and requirements, such as setback distances, minimum lot size, and soil type. Working with a qualified septic system contractor can help navigate these regulations and ensure a smooth, compliant installation process.
Site Evaluation and Soil Testing
A proper site evaluation and soil testing are essential for determining the suitability of a property for a mound septic system. A qualified professional, such as a soil scientist or septic system contractor, should conduct a thorough site assessment, considering factors like topography, drainage, and proximity to water sources. This evaluation will help identify any potential issues, such as excessive slopes, flood-prone areas, or high water tables, that could impact the system's performance.
Soil testing is another vital step in the process. It involves collecting soil samples at various depths to assess the soil's permeability, texture, and structure. The results will help determine the appropriate size and design for the mound system and ensure that the treated wastewater can be adequately absorbed into the ground without contaminating nearby water sources.
Installation Process
The installation process for a mound septic system is complex and requires expertise in engineering, excavation, and plumbing. It typically involves the following steps:
Site preparation: Clearing and leveling the area where the mound will be constructed, ensuring proper drainage and suitable slopes.
Septic tank installation: Installing a septic tank to collect and separate solid waste from liquid waste.
Dosing chamber installation: Constructing a dosing chamber to distribute the liquid effluent evenly across the mound.
Mound construction: Building the mound with layers of sand, gravel, and topsoil, following the specific design tailored to the site conditions and local regulations.
Piping installation: Embedding a network of pipes within the mound to facilitate the distribution and absorption of effluent.
System activation: Once the installation is complete, the contractor will activate the system, ensuring proper functioning and compliance with regulations.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Like any septic system, mound systems can experience issues that require troubleshooting and maintenance. Some common problems include:
Uneven distribution of effluent: This can be caused by clogged pipes or a malfunctioning dosing pump. Regular inspections and cleaning of the pipes can help prevent this issue.
Erosion: Heavy rain or snow can cause soil erosion on the mound, potentially exposing the underlying pipes and gravel. Repairing eroded areas and establishing appropriate vegetation can help stabilize the mound.
Odors: Foul odors around the mound could indicate a problem with the septic tank or the mound itself. In such cases, consult a professional to identify and address the issue.
Comparing Mound Septic Systems with Other Wastewater Treatment Options
When evaluating wastewater treatment options, it's essential to consider alternatives to mound septic systems. These may include conventional septic systems, aerobic treatment units (ATUs), or connecting to a municipal sewer system. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the property's specific needs and constraints.
Conventional septic systems are typically more affordable and straightforward to install than mound systems but may not be suitable for properties with shallow soil, high water tables, or bedrock near the surface. In contrast, ATUs are more expensive than both conventional and mound systems but offer improved treatment efficiency and can be a suitable option for smaller lots with limited space.
Connecting to a municipal sewer system is another option for homeowners who have access to public infrastructure. This choice can eliminate the need for on-site wastewater treatment and its associated maintenance. However, connection costs, ongoing utility fees, and local regulations should be considered when evaluating this alternative.
Impact on Property Value
The presence of a mound septic system on a property can impact its value and resale potential. While some buyers may appreciate the system's environmental benefits and adaptability to challenging site conditions, others may be deterred by the higher installation and maintenance costs, aesthetic concerns, or potential issues with system performance.
To minimize any negative impact on property value, homeowners should maintain their mound systems properly, address any aesthetic concerns with landscaping, and ensure that all necessary permits and documentation are in order. These measures can help demonstrate to potential buyers that the mound system is an asset rather than a liability.
Signs of Mound Septic System Failure
Recognizing the warning signs of a malfunctioning or failing mound septic system can help homeowners address issues before they escalate into more significant problems. Some indicators of system failure include:
Wet spots or standing water on or near the mound: This could be a sign of poor absorption or a leak in the system, requiring immediate attention.
Foul odors around the mound or septic tank: Persistent odors may indicate an issue with the septic tank or the mound itself, such as a clog or inadequate treatment.
Slow drains or plumbing backups: These issues can be a sign of an overloaded or failing septic system, potentially requiring professional intervention to resolve.
Lush, unusually green vegetation around the mound: This could be a sign of nutrient-rich effluent surfacing, indicating that the system is not effectively treating and absorbing wastewater.
If you notice any of these warning signs, it's essential to consult with a professional septic system contractor to diagnose and address the issue, ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of your mound septic system.
In conclusion, mound septic systems offer an adaptable and environmentally friendly wastewater treatment option for properties with challenging site conditions. By understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and essential maintenance practices, homeowners can make informed decisions about their wastewater treatment needs. By being aware of permits, regulations, and potential impacts on property value, you can ensure the success of your mound septic system and protect your investment in your property.
6. Conclusion
Mound septic systems offer a versatile and environmentally friendly solution for properties with challenging site conditions. By understanding their unique features, benefits, and maintenance requirements, you can ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your system. If you're considering installing a mound septic system, consult with a professional contractor to assess your property's suitability and design the best system for your needs.
.png) |
| Septic Tank Pumping Service |
.png)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment