DIY Septic Tank Maintenance
.png) |
| DIY Septic Tank Maintenance - its not so glamorous to do |
Introduction to DIY Septic Tank Maintenance
Understanding Septic Tank Systems
Septic tank systems are underground wastewater treatment structures commonly used in rural areas without centralized sewer systems. They consist of two main components: a septic tank and a drainfield. The septic tank is a watertight container made from concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene, designed to hold wastewater long enough for solids to settle out and form sludge, while the oil and grease float to the surface as scum. The drainfield, also known as a leach field or soil absorption system, is a series of perforated pipes laid in gravel-filled trenches or beds. It treats the wastewater by allowing it to slowly trickle into the soil, where it is naturally filtered and broken down by microorganisms.
When you maintain your septic tank system properly, you ensure its longevity, prevent environmental contamination, and avoid expensive repairs or replacements. Regular maintenance is vital to keeping your septic system functioning at peak performance. A well-maintained septic tank system can last for decades, saving you money and protecting your property's value
With over four decades of running our own septic tank company, my wife Jeane and I have encountered just about every situation you can think of with septic tanks. Now, in our later years, we're eager to share our extensive knowledge and help others who want to learn more about our favorite subject, septic tanks.Understanding Septic Tank Systems
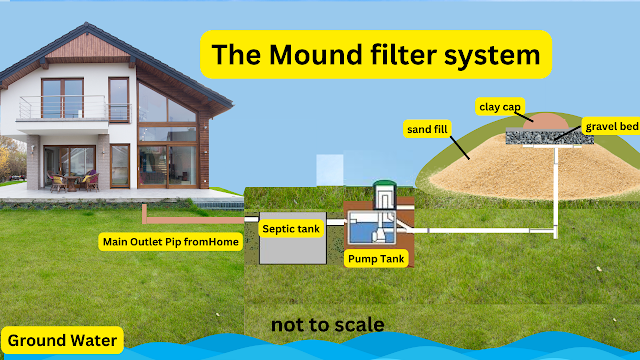
A septic tank system is a private, on-site wastewater treatment system commonly used in rural areas where centralized sewer systems are not available. It consists of two main components: the septic tank and the drainfield. The septic tank is a watertight container made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene, which holds and treats wastewater from your home. The drainfield is a series of perforated pipes buried in the ground, designed to disperse the treated wastewater into the soil.
The septic system operates based on natural biological processes. Bacteria break down organic waste in the wastewater, turning it into liquid and gaseous byproducts. Solids that cannot be broken down settle at the bottom of the tank, forming a layer of sludge. The liquid wastewater, or effluent, exits the tank through an outlet pipe and flows into the drainfield, where it is gradually absorbed into the soil.
Properly designed, installed, and maintained septic systems are an efficient and environmentally friendly option for wastewater treatment. However, inadequate maintenance or system failures can lead to contamination of groundwater and surface water, posing risks to public health and the environment.
Types of Septic Tanks
There are several types of septic tanks available, each with its unique characteristics and suitability for different applications:
Concrete septic tanks: Concrete septic tanks are durable, long-lasting, and heavy. They are typically preferred for their strength and longevity. However, they may develop cracks or leaks Properly designed, installed, and maintained septic systems are an efficient and environmentally friendly option for wastewater treatment. However, inadequate maintenance or system failures can lead to contamination of groundwater and surface water, posing risks to public health and the environment.
When considering a septic system, it's essential to understand the different types available and their respective components. The most common type is the conventional system, which includes a septic tank and a drainfield. The septic tank holds and treats wastewater from your home, while the drainfield disperses the treated wastewater into the soil.
An alternative to the conventional system is the aerobic treatment unit (ATU). This system uses oxygen to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria, which break down waste more quickly and efficiently than anaerobic bacteria found in conventional systems. ATUs are typically used in areas where conventional systems are not suitable due to environmental factors or regulatory requirements.
Another type of septic system is the mound system, which is designed for use in areas with shallow soil or high water tables. The mound system features a septic tank and a specially constructed mound of sand and gravel, through which the treated wastewater is dispersed. The mound provides additional treatment and filtration of the wastewater before it enters the soil.
Chamber systems are also a popular choice for septic systems, particularly in areas with difficult soil conditions or limited space. These systems use a series of chambers to distribute the wastewater evenly across the drainfield, promoting efficient treatment and reducing the risk of system failure.
Regardless of the type of septic system you choose, proper installation and maintenance are critical to ensuring its effectiveness and longevity. Regular inspections, pumping, and adherence to best practices for waste disposal and water conservation can help prevent costly repairs and protect your property's value.
In conclusion, understanding septic tank systems is essential for homeowners in rural areas who rely on these systems for wastewater treatment. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of systems and their components, you can make an informed decision about the best option for your property and ensure the proper care and maintenance of your system.
Types of Septic Tanks
There are several types of septic tanks available in the market, each designed to cater to specific needs and environmental factors. Knowing the different types of septic tanks and their unique characteristics can help you make an informed decision when selecting a suitable septic tank for your property.
Concrete septic tanks: Concrete septic tanks are the most common type of septic tanks and are preferred for their durability and strength. Made from reinforced concrete, these tanks can last for several decades if properly maintained. However, they can develop cracks or leaks over time and may require periodic inspection and repair to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, due to their weight, concrete septic tanks can be more challenging to install and may require specialized equipment.
Fiberglass septic tanks: Fiberglass tanks are lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making them an attractive alternative to concrete tanks. They are less susceptible to cracking and leaking, and their smooth interior surfaces help prevent the buildup of sludge. However, fiberglass tanks can be more expensive than other options and may be prone to damage from shifting soil or heavy loads placed on the ground above the tank.
Polyethylene septic tanks: Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), these tanks are lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to corrosion. Polyethylene tanks are also resistant to cracking, making them a suitable option for areas with unstable soil conditions. However, they may be more susceptible to damage from sunlight exposure and heavy loads placed on the ground above the tank. It's essential to install these tanks according to the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure their longevity and proper functioning.
Steel septic tanks: Although less common today, steel septic tanks were once widely used. They are lightweight and relatively easy to install. However, steel tanks have a shorter lifespan due to their susceptibility to rust and corrosion. The structural integrity of these tanks can be compromised over time, leading to leaks and potential system failures. For this reason, steel septic tanks are generally not recommended for new installations.
Advanced treatment systems: In addition to the traditional septic tank types, there are advanced treatment systems that provide additional levels of wastewater treatment before the effluent is dispersed into the drainfield. These systems typically include aerobic treatment units (ATUs), which use oxygen to promote the growth of aerobic bacteria for more efficient waste breakdown. Other advanced treatment systems, such as textile filters or recirculating sand filters, provide additional filtration and treatment of wastewater to meet higher environmental standards or specific regulatory requirements.
 |
| DIY Septic Tank Maintenance get basics right like the size of septic tank for your household |
Proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to best practices for waste disposal and water conservation are crucial for the optimal performance of your septic tank, regardless of its type. By understanding the different types of septic tanks and their unique characteristics, you can make an informed decision that best meets the needs of your property and contributes to a healthier environment.
How Septic Tanks Work
A septic tank is an essential component of an on-site wastewater treatment system. It is designed to hold and treat wastewater from your home, allowing solids to settle and separate from the liquid effluent. In this section, we will discuss the key processes that take place inside a septic tank and how they contribute to the effective treatment of wastewater.
Inlet and outlet pipes: Wastewater from your home enters the septic tank through the inlet pipe. The pipe's design and placement ensure that the incoming wastewater is distributed evenly within the tank, minimizing turbulence and promoting the separation of solids and liquids. The treated liquid effluent exits the tank through the outlet pipe, which is connected to the drainfield.
Separation of solids and liquids: Inside the septic tank, the wastewater undergoes a separation process. Heavier solids sink to the bottom, forming a layer of sludge, while lighter materials like grease and oil float to the top, forming a layer of scum. The relatively clear liquid in the middle, called effluent, is eventually discharged into the drainfield for further treatment.
Anaerobic digestion: The septic tank provides an environment for anaerobic bacteria, which thrive in the absence of oxygen. These bacteria break down the organic matter in the wastewater, converting it into simpler compounds, such as methane, carbon dioxide, and water. This process helps reduce the volume of solids in the tank and produces a partially treated effluent that can be safely dispersed into the drainfield.
Retention time: An essential aspect of septic tank function is the retention time, which refers to the amount of time the wastewater spends inside the tank. A longer retention time allows for more efficient separation of solids and liquids and more thorough digestion of organic matter by anaerobic bacteria. The size of the septic tank and the volume of wastewater generated by your household influence the retention time.
Sludge and scum Over time, the sludge and scum layers in the septic tank will build up as the anaerobic bacteria can only break down a portion of the organic matter. Regular maintenance, including periodic pumping of the septic tank, is necessary to remove these accumulated solids and prevent system failure.
Effluent quality: The quality of the effluent exiting the septic tank is crucial to the overall performance of the septic system. Although the effluent has undergone partial treatment within the tank, it still contains a significant amount of pollutants and pathogens. The drainfield serves as the secondary treatment component, where the effluent is further treated and filtered by the soil before entering the groundwater.
T-shaped baffles: To prevent the scum layer from clogging the outlet pipe, most septic tanks are equipped with T-shaped baffles. These baffles help maintain a clear path for the effluent to exit the tank while keeping the scum layer and any floating debris away from the outlet pipe.
In summary, septic tanks play a critical role in on-site wastewater treatment by providing a controlled environment for the separation of solids and liquids, as well as anaerobic digestion of organic matter. Proper maintenance, including regular inspections and pumping, is crucial to ensure the septic tank functions effectively and prolongs the life of your septic system.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your septic system is essential for its proper functioning, longevity, and environmental safety. Neglecting maintenance can lead to system failures, costly repairs, and potential contamination of groundwater and surface water. In this section, we will discuss the key reasons why regular maintenance is vital for your septic system.
Prevent system failure: A well-maintained septic system can last for decades, while a neglected system may fail in just a few years. Regular maintenance helps prevent system failures by ensuring that the septic tank does not become overfilled with solids, which can clog the drainfield and lead to sewage backups or groundwater contamination.
Protect public health and the environment: A failing septic system can pose serious risks to public health and the environment. Leaking or overflowing septic tanks can contaminate nearby groundwater and surface water sources with harmful pathogens and pollutants. Regular maintenance helps ensure that your system is operating effectively, reducing the risk of contamination.
Prolong the life of your septic system: Regular maintenance, such as pumping the septic tank and inspecting the drainfield, can help identify and address potential issues before they become significant problems. This proactive approach can help prolong the life of your septic system and protect your investment.
Save money on repairs: Addressing minor issues during routine maintenance is usually more cost-effective than dealing with major system failures. Regular maintenance can help you avoid costly emergency repairs or even the need for a complete system replacement.
Maintain property value: A well-maintained septic system is an asset to your property, while a failing system can significantly reduce its value. Regular maintenance can help ensure that your septic system remains in good working order, protecting your property's value and making it more attractive to potential buyers.
In conclusion, regular maintenance is essential for the proper functioning, longevity, and environmental safety of your septic system. By investing in routine inspections, pumping, and preventative measures, you can protect your investment, safeguard public health and the environment, and maintain your property's value.
Benefits of Maintaining Your Septic Tank
There are several benefits to maintaining your septic tank and septic system regularly. In this section, we will discuss some of the most significant advantages of keeping your septic tank well-maintained.
Cost savings: Regular maintenance can help you avoid costly repairs or replacements by addressing minor issues before they escalate into more significant problems. For example, pumping your septic tank every 3-5 years, depending on your household size and water usage, can prevent the buildup of sludge and scum, which can cause system failure if left unaddressed.
Longer lifespan: A well-maintained septic system can last for several decades, while a neglected system may fail much sooner. By investing in routine maintenance, you can prolong the life of your septic system and avoid the costly and disruptive process of replacing it prematurely.
Environmental protection: A properly functioning septic system treats wastewater effectively, protecting the surrounding environment from contamination. Regular maintenance ensures that your septic system continues to operate efficiently, reducing the risk of groundwater and surface water pollution.
Public health: A failing septic system can pose risks to public health by allowing harmful pathogens and pollutants to contaminate nearby water sources. Regular maintenance helps ensure that your system is operating effectively, minimizing the risk of contamination and protecting the health of your family and neighbors.
Improved system performance: Regular maintenance, including inspecting and cleaning various components of your septic system, can help optimize its performance. For example, checking the T-shaped baffles in your septic tank can ensure that they are functioning correctly, preventing the scum layer from clogging the outlet pipe and causing backups.
Compliance with regulations: In many jurisdictions, regular septic system maintenance is required by law to protect public health and the environment. By adhering to these regulations, you can avoid fines or penalties and contribute to a healthier community.
Preserve property value: A well-maintained septic system is an asset to your property, while a failing system can significantly reduce its value. By investing in regular maintenance, you can protect your property's value and make it more attractive to potential buyers should you decide to sell.
In conclusion, maintaining your septic tank and septic system regularly offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, longer system lifespan, environmental protection, public health, improved system performance, compliance with regulations, and preserving your property's value. By investing in routine maintenance, you can enjoy these benefits and ensure the continued effective operation of your septic system.
 |
| DIY Septic tank Maintenance check for signs action is needed |
Signs of Septic Tank Issues
Being able to recognize the signs of potential septic tank issues is crucial for addressing problems before they become more serious and costly. In this section, we will discuss some common indicators of septic tank problems that homeowners should be aware of.
Slow drains or backups: If you notice that the drains in your home are draining slowly, or you experience sewage backups, this may be an indication that your septic tank is full or that there is a blockage in your system.
Foul odors: Unpleasant smells around your septic tank, drainfield, or inside your home can be a sign of a failing septic system. This may indicate that your septic tank is overfilled or that the drainfield is not effectively treating the wastewater.
Soggy ground or standing water: If you notice soggy ground or standing water around your septic tank or drainfield, this may indicate that your system is not effectively dispersing the wastewater. This can be a sign of a clogged drainfield or a failing septic system.
Lush, green grass over the drainfield: While it's normal for the grass over your drainfield to be slightly greener than the surrounding area, excessively lush and green grass may indicate that your septic system is not effectively treating the wastewater, causing excess nutrients to be released into the soil.
Gurgling sounds in the plumbing: If you hear gurgling sounds coming from your plumbing system when you flush the toilet or use sinks and showers, this may be a sign of a problem with your septic system. It could indicate that your septic tank is full, or there is a blockage in the pipes leading to or from the tank.
Frequent need for pumping: If you find yourself needing to pump your septic tank more frequently than the recommended 3-5 year interval, this could be a sign of a problem with your septic system. It may indicate that the system is not effectively treating the wastewater, or there could be an issue with the drainfield.
High levels of nitrate or coliform bacteria in well water: If you rely on well water and regularly test it for contaminants, high levels of nitrate or coliform bacteria could be an indication of a failing septic system. This means that untreated wastewater may be contaminating your groundwater, posing a risk to your health and the environment.
By being aware of these signs of septic tank issues, you can take action to address problems before they become more severe and costly. Regular maintenance and inspections can help you catch potential issues early on and ensure the proper functioning and longevity of your septic system.
DIY Septic Tank Maintenance Tips
While it's essential to rely on professionals for certain aspects of septic system maintenance, such as pumping and inspections, there are several steps homeowners can take to help maintain their septic tanks and systems. Here are some DIY maintenance tips to help you care for your septic system:
Conserve water: Reducing the amount of water you use can help prevent overloading your septic system. Be mindful of your water usage by using water-efficient appliances, fixing leaks promptly, and avoiding running multiple water-intensive appliances simultaneously.
Proper waste disposal: Be cautious about what you put down your drains and toilets. Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, such as diapers, wipes, or feminine hygiene products, as they can clog your system. Also, avoid pouring grease or oil down the sink, as it can solidify and cause blockages.
Regularly inspect your system: Perform visual inspections of your septic tank and drainfield periodically. Look for signs of problems, such as foul odors, standing water, or lush, green grass over the drainfield.
Maintain your drainfield: Keep the area around your drainfield clear of trees and shrubs, as their roots can damage the pipes. Avoid driving or parking heavy vehicles on the drainfield, as this can compact the soil and damage the system.
Use septic-safe products: Choose household cleaning products and detergents that are septic-safe, as some chemicals can be harmful to the beneficial bacteria in your septic tank.
Keep records: Maintain records of your septic system maintenance, including pumping dates, inspections, and any repairs. This can help you stay on top of your system's needs and provide valuable information for future maintenance or potential buyers if you sell your property.
While these DIY maintenance tips can help you care for your septic system, it's important to remember that professional inspections and pumping are still essential for maintaining your system's health and longevity.
Inspecting Your Septic Tank
Regular septic tank inspections are a critical component of proper septic system maintenance. These inspections can help identify potential issues before they become serious problems and ensure that your system is functioning effectively. Here are some key aspects of septic tank inspections:
Frequency of inspections: It's generally recommended to have your septic tank inspected every 3-5 years, depending on the size of your tank and the number of people in your household. Some local regulations may require more frequent inspections, so be sure to check the requirements in your area.
Professional inspections: While you can perform some visual inspections yourself, it's essential to rely on a professional septic service provider for thorough inspections. They have the necessary expertise, tools, and equipment to accurately assess your system's condition and address any issues.
What to expect during an inspection: During a septic tank inspection, the service provider will typically check the following:
The overall condition of the tank and its components, including the inlet and outlet pipes, T-shaped baffles, and access ports.
The levels of sludge and scum in the tank to determine if pumping is necessary.
The integrity of the tank's walls and lids, looking for cracks or other signs of damage.
The drainfield's condition, checking for signs of saturation or failure, such as standing water, odors, or overly lush vegetation.
Addressing issues: If the inspection reveals any issues with your septic tank or system, the service provider will recommend the necessary repairs or maintenance actions to address the problems. This may include pumping the tank, repairing or replacing damaged components, or addressing issues with the drainfield.
Record-keeping: Keep a record of your septic tank inspections, including the date, any findings, and any actions taken. This information can be helpful for future maintenance and can be valuable for potential buyers if you decide to sell your property.
In conclusion, regular septic tank inspections are a crucial aspect of maintaining your septic system. By scheduling professional inspections every 3-5 years and addressing any issues that arise, you can ensure the proper functioning and longevity of your system.
.png) |
| DIY Septic Tank Maintenance - Pumping your own Tank Not Really! |
Pumping Your Septic Tank
Pumping your septic tank is an essential maintenance task that helps prevent system failures and prolongs the life of your septic system. In this section, we will discuss the importance of pumping your septic tank and provide some guidelines for how often it should be done.
Why pumping is necessary: Over time, the sludge and scum layers in your septic tank will accumulate, as the anaerobic bacteria can only break down a portion of the organic matter. Pumping your septic tank removes these accumulated solids, preventing them from entering the drainfield and causing system failure.
Frequency of pumping: The frequency at which your septic tank should be pumped depends on several factors, including the size of your tank, the number of people in your household, and your water usage habits. Generally, it's recommended to pump your septic tank every 3-5 years. However, you may need to pump more frequently if you have a smaller tank, a large household, or use a significant amount of water.
Signs your tank needs pumping: In addition to regular pumping intervals, there are some signs that your septic tank may need pumping sooner than expected. These include slow-draining sinks and toilets, sewage backups, foul odors near the tank or drainfield, or a sudden increase in the lushness of the grass over the drainfield.
Professional pumping services: It's essential to rely on a professional septic service provider for pumping your septic tank. They have the necessary equipment and expertise to safely and effectively remove the solids from your tank and dispose of them in accordance with local regulations.
In summary, pumping your septic tank is a critical maintenance task that helps prevent system failures and prolongs the life of your septic system. By adhering to regular pumping intervals and watching for signs that your tank may need pumping sooner than expected, you can ensure the continued effective operation of your system.
Proper Waste Disposal
Proper waste disposal is crucial for maintaining the health and efficiency of your septic system. By being mindful of what you put down your drains and toilets, you can help prevent clogs, system overloads, and damage to your septic tank and drainfield. Here are some guidelines for proper waste disposal in homes with septic systems:
Toilet waste: Only flush human waste and toilet paper down the toilet. Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, such as diapers, wipes, feminine hygiene products, or dental floss, as they can clog your septic system and lead to backups or system failure.
Kitchen waste: Be cautious about what you put down your kitchen sink. Avoid pouring grease, oil, or fats down the drain, as they can solidify and cause blockages. Use a strainer in your sink to catch food scraps, and dispose of them in the trash or a compost bin.
Chemical waste: Certain chemicals, such as paints, solvents, and pesticides, can be harmful to the beneficial bacteria in your septic tank and should not be poured down the drain. Dispose of these chemicals according to local regulations and guidelines.
Cleaning products: Choose septic-safe cleaning products and detergents that are biodegradable and free of harmful chemicals. Some products can be detrimental to the bacteria in your septic tank, reducing its ability to break down organic matter.
Garbage disposal use: While garbage disposals can be convenient, they can also contribute to an increased amount of solid waste in your septic tank. Use your garbage disposal sparingly, and be mindful of the types of food waste you put into it. Avoid disposing of fibrous or hard-to-break-down materials, such as coffee grounds, eggshells, and bones.
By following these proper waste disposal guidelines, you can help prevent clogs, system overloads, and damage to your septic system, ensuring its continued effective operation.
Water Conservation
Water conservation is essential for maintaining a healthy septic system, as excessive water usage can overload your system and lead to system failure. Here are some tips for conserving water in homes with septic systems:
Fix leaks promptly: Leaking faucets, toilets, or pipes can waste a significant amount of water and put unnecessary strain on your septic system. Be sure to fix any leaks as soon as you notice them.
Use water-efficient appliances: Invest in water-efficient appliances, such as low-flow toilets, faucet aerators, and high-efficiency washing machines and dishwashers. These appliances can help reduce your water usage and lessen the load on your septic system.
Spread out laundry loads: Instead of doing multiple loads of laundry in one day, spread them out over the week to help reduce the strain on your septic system. Additionally, only run your washing machine and dishwasher when they are full to maximize water efficiency.
Take shorter showers: Reducing the amount of time you spend in the shower can help conserve water and reduce the load on your septic system. Consider installing a low-flow showerhead to further decrease water usage.
Don't let water run unnecessarily: Be mindful of your water usage habits, and avoid letting water run when it's not needed. For example, turn off the faucet while brushing your teeth, and only run the water when you're ready to rinse.
By conserving water and being mindful of your water usage habits, you can help reduce the strain on your septic system and ensure its continued effective operation.
Maintaining Drainfield and Landscaping
The drainfield is a critical component of your septic system, as it's responsible for dispersing the treated wastewater back into the soil. Proper drainfield maintenance and landscaping are essential for ensuring the effective operation and longevity of your septic system. Here are some tips for maintaining your drainfield and the surrounding landscape:
Keep the area clear: Avoid planting trees or large shrubs near your drainfield, as their roots can grow into the pipes and cause damage. Instead, plant grass or shallow-rooted plants in the area to help with soil erosion control.
Avoid compaction: Do not drive or park heavy vehicles on or near the drainfield, as this can compact the soil and damage the pipes. Additionally, avoid placing heavy objects, such as sheds or pools, on or near the drainfield.
Maintain proper grading: Ensure that the soil around your drainfield is graded correctly, allowing water to flow away from the area. This can help prevent ponding or saturation, which can lead to system failure.
Monitor for signs of problems: Regularly inspect your drainfield for signs of issues, such as standing water, foul odors, or overly lush vegetation. If you notice any of these signs, contact a septic professional for an inspection and assessment.
Divert rainwater: Make sure that your home's gutter system is designed to divert rainwater away from the drainfield. Excessive water in the area can saturate the soil and reduce the drainfield's ability to effectively disperse treated wastewater.
By following these maintenance and landscaping tips, you can help protect your drainfield and ensure the effective operation of your septic system.
Spotting and Addressing Problems
Being proactive in spotting and addressing potential septic system problems is crucial for maintaining your system's health and longevity. Here are some tips for spotting and addressing issues with your septic system:
Know the signs of problems: Familiarize yourself with the common signs of septic system issues, such as slow-draining sinks and toilets, sewage backups, foul odors, or lush vegetation over the drainfield.
Regular maintenance and inspections: Schedule regular septic system maintenance, including professional inspections and tank pumping, to help catch potential issues before they become serious problems.
Address issues promptly: If you notice any signs of septic system problems, contact a septic professional as soon as possible to assess the situation and recommend the necessary repairs or maintenance actions.
Educate household members: Ensure that all members of your household understand the importance of proper waste disposal and water conservation to help prevent septic system issues.
By being proactive in spotting and addressing potential septic system problems, you can help prevent more severe and costly issues down the line.
When to Call a Professional
While there are many DIY maintenance tips for caring for your septic system, there are times when it's essential to call a professional. Here are some situations in which you should seek the assistance of a septic professional:
Routine inspections and pumping: Schedule regular septic tank inspections and pumping every 3-5 years, or as needed based on your system's size and usage.
Signs of problems: If you notice any signs of septic system issues, such as slow-draining sinks and toilets, sewage backups, or foul odors, contact a septic professional for an inspection and assessment.
System repairs or replacements: If your septic system requires repairs or replacements, such as fixing or replacing damaged pipes, T-shaped baffles, or the tank itself, it's essential to rely on a professional with the necessary expertise and equipment.
By knowing when to call a professional and seeking their assistance when needed, you can help ensure the proper functioning and longevity of your septic system.
Septic Tank Emergencies
In some cases, septic system issues can escalate into emergencies that require immediate attention. Here are some examples of septic tank emergencies and what to do if you encounter them:
Sewage backup: If you notice sewage backing up into your home or surfacing near the septic tank or drainfield, this is a sign of a severe problem that needs immediate attention. Turn off the water supply to your home and contact a septic professional as soon as possible.
Foul odors: If you smell strong, persistent sewage odors near your septic tank or drainfield, it could indicate a leak or system failure. Contact a septic professional immediately to assess the situation and recommend the necessary repairs.
Collapse or damage: If you suspect that your septic tank has collapsed or been damaged, perhaps due to heavy vehicle traffic or other factors, it's crucial to call a professional immediately. Do not attempt to access or repair the tank yourself, as this can be hazardous.
Drainfield flooding: If your drainfield becomes flooded or saturated with water, it could indicate a system failure or other issue. Turn off the water supply to your home and contact a septic professional for an assessment and recommended course of action.
In the event of a septic tank emergency, it's essential to act quickly and seek the assistance of a professional. This can help minimize the damage and potential health risks associated with septic system failures.
In conclusion, maintaining your septic system is vital for the proper functioning and longevity of your system. By following the tips and guidelines provided in this article, you can help prevent issues and ensure the continued effective operation of your septic system. Regular maintenance, proper waste disposal, water conservation, and knowing when to call a professional are all critical aspects of septic system care. By being proactive in caring for your system, you can save time, money, and potential headaches down the line.

.png)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment