Septic Tank Diagram
 |
| Sceptic Tank Diagram |
Septic Tank Diagram: A Must-Have Tool for Every Homeowner
Having a septic tank diagram is crucial when troubleshooting issues with your sewage system. However, understanding and interpreting the diagram can be challenging. In this guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of reading a septic tank diagram. We will examine each component of the diagram and its function within the system. Additionally, we will address common problems that may arise with your septic system.
We offer you our Decades of Septic Tank Experience
Embarking on the journey of managing septic systems can be overwhelming, but worry not! With decades of combined experience, my partner Jeane and I have encountered and overcome numerous challenges in this intricate domain.
Our primary objective is to impart our extensive knowledge to both seasoned septic system owners and newcomers alike. Through this blog, we are committed to providing valuable insights and tips on various topics.
Our mission is to assist you in unraveling the mysteries of maintaining an environmentally friendly safe septic system that operates optimally for the long term. Join us on this enlightening adventure as we explore the fascinating world of septic systems! We hope you like our Septic Tank Diagram and where it all starts.
What Does a Diagram Look Like?
A typical septic tank diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the tank and the intricate system that manages your waste. By reviewing this information, you can identify areas where potential problems might occur.
For instance, issues such as flooding or unpleasant odors can indicate specific problems in your system. If your tank is experiencing certain issues, you may notice wastewater backing up into your sink. By identifying the problematic area through the diagram, you can avoid the need for extensive digging, simplifying the troubleshooting process.
Apart from problem diagnosis, the septic Tank Diagram is essential for planning property projects efficiently. Knowing the location of different components of the septic system is crucial to avoid damage when driving or constructing over those areas. As you can see above this is a typical Septic Tank Diagram. Of course, they are other types of Septic Tank Diagrams that we will feature in this article. For the main six types of Septic Systems look at our comparison of them in this post here
Understanding the Septic Tank Diagram
What Does a Septic Tank Look Like?
The septic tank is a central component of the septic system and plays a vital role in waste treatment. When looking at the Septic Tank Diagram you can see It is typically cylindrical or square in shape. Inside the tank, various types of waste are present. The upper layer, known as scum, consists of substances like soap and oils. In the middle, liquid waste, including greywater from sinks, toilets, and appliances, is found. The bottom layer contains more solid waste.
Some septic systems feature a divider system to regulate the ratio of wastewater, scum, and sludge. This configuration helps manage the flow of the system, preventing overflow. Although we show in this Septic Tank Diagram your may vary from this although the principal is the same
Having a septic tank diagram is crucial when troubleshooting issues with your sewage system. However, understanding and interpreting the diagram can be challenging. In this guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of reading a septic tank diagram. We will examine each component of the diagram and its function within the system. Additionally, we will address common problems that may arise with your septic system.
What Does a Diagram Look Like?
A typical septic tank diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the tank and the intricate system that manages your waste. By reviewing this information, you can identify areas where potential problems might occur.For instance, issues such as flooding or unpleasant odors can indicate specific problems in your system. If your tank is experiencing certain issues, you may notice wastewater backing up into your sink. By identifying the problematic area through the diagram, you can avoid the need for extensive digging, simplifying the troubleshooting process.
Apart from problem diagnosis, the septic Tank Diagram is essential for planning property projects efficiently. Knowing the location of different components of the septic system is crucial to avoid damage when driving or constructing over those areas.
Understanding the Septic Tank Diagram
What Does a Septic Tank Look Like? The septic tank is a central component of the septic system and plays a vital role in waste treatment. When looking at the Septic Tank Diagram you can see It is typically cylindrical or square in shape. Inside the tank, various types of waste are present. The upper layer, known as scum, consists of substances like soap and oils. In the middle, liquid waste, including greywater from sinks, toilets, and appliances, is found. The bottom layer contains more solid waste.Some septic systems feature a divider system to regulate the ratio of wastewater, scum, and sludge. This configuration helps manage the flow of the system, preventing overflow. Although we show in this Septic Tank Diagram yours may vary from this although the principal is the same
Drinking Water and Wastewater
To ensure safety, it is essential to maintain a minimum distance of fifty feet between your septic system and your drinking water source. Failure to comply with this requirement can lead to contamination of your drinking water with wastewater, posing severe health risks.If you purchase a property and find that the septic system is not at least fifty feet away from your well, it is advisable to have a new system installed and consult professionals to remove the old one.
Using Wastewater – Avoid It
If you discover that your drinking water is contaminated, it is crucial to immediately stop using it. Avoid bathing in or washing anything with the tainted water, and refrain from drinking it. Contact professionals promptly for assistance. Using wastewater-contaminated water can have severe health consequences, even when used for tasks like laundry or dishwashing.
Septic System Configurations
In this Septic Tank Diagram it shows but it can differ in terms of different configurations depending on the living situation. In suburban areas, the septic system is often connected to multiple households after the septic tank. On the other hand, rural areas typically have septic systems dedicated solely to individual homes. Understanding the type of system you have is crucial for effectively managing any septic tank issues.If you live in a suburban-like area, ensure that the septic tank is your responsibility before attempting to address a problem. It may be the responsibility of your landlord or landowner. In such cases, notify them immediately if any issues arise.
Avoid Overloading Your Septic System
One common cause of septic system overload is flushing excessive solid waste, such as food particles. Another factor is the increased usage of appliances like washing machines. Both actions can strain the septic system, leading to problems.
Septic Tank Cleanout
Cleaning out your septic tank yourself can be dangerous, especially when it is overflowing. The fumes alone pose health hazards and should not be underestimated. It is always recommended to work with professionals to ensure the proper resolution of septic tank issues. They are equipped to handle the task of cleaning out your septic tank safely and effectively. |
| Not on a Septic Tank Diagram But there can be a real danger |
Understanding the Drain Field
A vital component of your septic tank system is the drain field. It consists of a network of perforated pipes buried underground in gravel beds, serving as a soil absorption system. These pipes allow the effluent (treated wastewater) to drain into the soil, where it undergoes natural filtration before reentering the groundwater.
Are Drain Fields Necessary?
Yes, drain fields are essential for a properly functioning septic system. They ensure the proper distribution of wastewater and prevent backups, allowing for effective wastewater management. The drain field directs the wastewater away from the septic tank and your living area.
Consequences of Not Having a Drain Field
Without a drain field, your septic system will encounter significant problems. Wastewater will back up and eventually flood your home, leading to hazardous and unsanitary conditions. Installing or maintaining a drain field is crucial to ensure the smooth operation of your septic system. If you are unsure whether you have a drain field, consulting your septic tank diagram can provide the necessary information. It will also help you locate the drain field for future maintenance or repairs.
Septic Filter (Effluent Filter)
The septic filter, also known as an effluent filter, is situated inside the septic tank. It is important to note that attempting to fix or replace this filter yourself is not recommended. The interior of a septic tank is hazardous, and professional assistance should always be sought if you suspect any issues with the filter. The filter is positioned before the drain field pipes.
The purpose of the filter is to prevent solid waste from entering the drain pipes, ensuring that only treated effluent flows into the drain field. By doing so, the filter helps maintain the integrity of the surrounding ground and groundwater, preventing contamination.
Pump Tanks
Pump tanks are additional small tanks installed in some septic systems. While not mandatory, they provide added benefits that optimize the functioning of your septic system. Pump tanks help prevent solids from entering the system, reducing the likelihood of clogs in the drain field. Furthermore, pump tanks have the ability to activate and deactivate the system. Many models even include high water warning systems, alerting you when there are issues with your system.
The Distribution Box
The distribution box plays a crucial role in equalizing the distribution of wastewater among the drain field lines. It ensures efficient wastewater distribution, preventing backups and promoting the smooth operation of your septic system. By removing wastewater from the septic tank and evenly distributing it, the distribution box creates space for additional solid waste. Without a distribution box, the septic tank would fill up quickly, leading to potential problems. |
| a septic distribution box |
The Leach Drain Field
Another essential component of your septic tank system is the leach drain field. This section receives effluent from the septic tank and consists of a network of drain pipes. The effluent percolates through the soil, undergoing natural filtration and purification processes before rejoining the water system. The leach drain field plays a critical role in ensuring that only treated and purified water enters the water system, while preventing untreated wastewater from contaminating drinking water sources.
Importance of Home Inspections
While a home inspection may provide confidence in the overall condition of your property, it typically does not cover the sewer or septic system. These systems are separate from the main structure of your home, and it is essential to have your septic system inspected independently to identify any potential issues.Even if your home has passed inspection, problems in your septic system may still exist. To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your septic system, regular maintenance is key. Issues such as septic system backups or septic tank flooding can arise, emphasizing the importance of staying vigilant and addressing problems promptly.
Scheduled inspections and pump-outs are recommended to maintain the effectiveness of your septic system. Professional septic service providers can assist in cleaning out your septic tank, identifying potential issues, and providing necessary repairs or maintenance.
Remember that your septic system is responsible for environmentally friendly waste management. Treat it with care and avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, chemicals, or excessive solids. Additionally, practicing water conservation and implementing water-saving measures can alleviate the strain on your septic system.
Components of a Septic Tank System
When it comes to understanding septic tank diagrams, it's crucial to familiarize ourselves with the various components that make up a septic tank system. While the article does touch on the septic tank itself, there are other essential elements worth exploring in more detail. Let's delve into these components to gain a comprehensive understanding of how they contribute to the overall functionality of a septic system.
Inlet and Outlet Pipes
One of the key components of a septic tank system is the network of inlet and outlet pipes. These pipes serve as the main conduits for the flow of wastewater into and out of the septic tank. The inlet pipe directs the wastewater from the plumbing system of the house into the tank, while the outlet pipe carries the treated effluent out of the tank and into the drain field.
Baffles
Baffles play a critical role in the proper functioning of a septic tank. They are essentially dividers or partitions within the tank that help regulate the flow of wastewater and separate the different layers of waste. Baffles ensure that the heavier solids settle at the bottom of the tank, while allowing the lighter scum to rise to the top. By preventing the scum and solids from escaping into the drain field, baffles help maintain the efficiency and longevity of the entire system.
Venting System
A well-designed septic tank system includes a venting system to facilitate the release of gases produced during the decomposition of waste. Vent pipes are installed to allow the escape of gases, such as methane and hydrogen sulfide, which are byproducts of the anaerobic digestion process within the tank. Proper ventilation not only helps prevent the build-up of potentially harmful gases but also ensures the optimal functioning of the system by maintaining the necessary balance of pressure.
By understanding the role of these components within a septic tank system, we can develop a clearer picture of how each part contributes to the overall functioning of the system. This knowledge becomes particularly valuable when interpreting septic tank diagrams and diagnosing potential issues that may arise.
Remember, a septic tank system is a complex network of interconnected components, and a holistic understanding of these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. With this knowledge in hand, we can better comprehend the intricacies of a septic tank diagram and make informed decisions regarding its upkeep.
In the following sections, we will explore common septic tank problems, regulatory considerations, maintenance practices, and more. Through an analytical lens, we will uncover valuable insights and practical tips to navigate the realm of septic tank diagrams. So, let's dive deeper and unravel the mysteries of this crucial wastewater management system.
Proper Maintenance and Care of a Septic Tank System
Maintaining a septic tank system is essential for its longevity and efficient operation. While the article briefly mentions the importance of maintenance and problem identification, let's delve into more specific guidance on regular maintenance tasks. By following these practices, you can ensure that your septic tank system remains in optimal condition for years to come.
Pumping the Tank
One of the most critical maintenance tasks for a septic tank is regular pumping. Over time, solid waste accumulates at the bottom of the tank, forming sludge that needs to be removed. If the sludge reaches a certain level, it can clog the system and lead to backups and other issues.
It is generally recommended to have a professional septic tank service pump the tank every three to five years, depending on the size of the tank and household usage. By pumping the tank, you remove the accumulated sludge, allowing the system to function efficiently and preventing potential problems down the line.
Inspecting the System
Regular inspections are crucial for identifying any issues or signs of potential problems in your septic tank system. It is advisable to have a professional inspect the system at least once a year. During the inspection, they will assess the condition of the tank, check for leaks, inspect the drain field, and ensure that all components are functioning properly.
Additionally, homeowners can also perform simple visual inspections themselves. Look for signs of wastewater backups, slow drains, or foul odors around the septic tank or drain field. These can be indications of underlying issues that require attention.
Using Additives
In some cases, using septic tank additives can be beneficial for maintaining a healthy and well-functioning system. Additives are designed to introduce beneficial bacteria and enzymes into the septic tank, aiding in the breakdown of solid waste and promoting efficient decomposition.
However, it is important to exercise caution when using additives. Not all additives are effective, and some may even be harmful to the system. Consult with a professional or follow manufacturer guidelines before using any additives to ensure they are suitable for your specific septic tank system.
Water Conservation
Conserving water usage in your household can also contribute to the proper maintenance of a septic tank system. Excessive water usage can overload the system and lead to backups and strain on the drain field. Implementing water-saving practices, such as fixing leaky faucets, using efficient appliances, and spacing out laundry and dishwashing loads, can help alleviate the strain on the system and prolong its lifespan.
By incorporating these maintenance practices into your routine, you can ensure the longevity and efficient operation of your septic tank system. Regular pumping, inspections, and proper water usage are key to preventing costly repairs and avoiding disruptions to your daily life.
Remember, when it comes to septic tank maintenance, it is always recommended to consult with professionals who have expertise in septic systems. They can provide personalized guidance based on the specific characteristics of your system, ensuring that you take the necessary steps to keep it in optimal condition.
Common Septic Tank Problems
While the article briefly mentions issues like flooding and odors, it is important to have a comprehensive understanding of the common problems that homeowners may encounter with their septic tank systems. By recognizing these issues, you can take proactive measures to address them and ensure the proper functioning of your system. Here are some of the most common septic tank problems:
1. Blockages
Blockages in the septic system can occur due to various reasons. Solid waste, debris, grease, or foreign objects that should not enter the system can clog the pipes, leading to backups and slow drains. Blockages can also occur within the septic tank itself, hindering the flow of wastewater and causing issues. Regular pumping, proper disposal practices, and avoiding flushing non-biodegradable materials are essential to prevent blockages.
2. Leaks
Leakage in the septic system can cause significant problems. It can occur in the pipes, tank, or connections, allowing wastewater to escape into the surrounding soil. Leaks not only contaminate the environment but can also lead to a foul odor, soggy areas in the yard, or even health hazards. Promptly addressing leaks and repairing any damaged components is crucial to prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of the system.
3. Drain Field Failures
The drain field is an integral part of the septic system responsible for the final treatment and disposal of effluent. Drain field failures can occur due to various reasons, including clogging, soil compaction, excessive water usage, or the growth of tree roots. Signs of drain field failure include wet areas in the yard, unpleasant odors, and slow-draining fixtures. If left unaddressed, drain field failures can lead to backups and system malfunctions, requiring extensive repairs or replacement.
4. Excessive Solids in the Tank
When the accumulation of solids in the septic tank exceeds its capacity, it can lead to problems. Over time, excessive solids can impede the treatment process and result in inadequate decomposition. This can lead to clogged pipes, backups, and potential damage to the drain field. Regular pumping, as recommended by professionals, helps prevent excessive solids buildup and ensures the system's efficient operation.
5. Tree Root Intrusion
The presence of trees near the septic system can pose a risk of tree root intrusion. As trees seek water sources, their roots can penetrate pipes and the septic tank, causing damage and obstruction. Tree roots can disrupt the flow of wastewater, leading to backups and system failures. If you have trees in close proximity to your septic system, regular monitoring and proactive root management measures are necessary.
By being aware of these common septic tank problems, homeowners can be proactive in addressing issues and seeking professional assistance when needed. Regular maintenance, timely repairs, and following proper usage and disposal practices are vital for preventing these problems and ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the septic system. Remember to consult with qualified septic system professionals for accurate diagnosis and appropriate solutions.
Troubleshooting and Problem Diagnosis in a Septic Tank System
 |
| Septic Tank Problems |
1. Tank Overflow
By examining the diagram, you can identify signs of tank overflow. If the diagram indicates that the liquid level in the tank is higher than normal or approaching the inlet pipe, it may indicate a problem. Tank overflow can be caused by blockages, excessive water usage, or a failure in the drain field. Look for visual cues that indicate high liquid levels in the diagram to address the issue before it leads to backups or system failures.
2. Drain Field Issues
The diagram can also provide valuable information about the drain field and potential problems associated with it. Look for signs of excessive liquid accumulation or pooling in the drain field area. This may indicate drainage issues, clogging, or soil compaction problems. In the diagram, if the drain field appears to be flooded or if there are signs of effluent backing up, it is essential to investigate further and seek professional assistance to prevent damage to the drain field and the overall system.
3. Damaged Components
Carefully examine the diagram for any indications of damaged or malfunctioning components within the septic tank system. Look for visual cues such as broken or cracked pipes, damaged baffles, or leaks in the tank. These issues can lead to system inefficiencies, leakage, and potential health hazards. Identifying damaged components in the diagram can help you direct your attention to the specific areas that require repair or replacement.
4. Unusual Odors or Wet Areas
While not directly visible in the diagram, the presence of unusual odors or wet areas around the septic tank or drain field can provide important clues about potential problems. Foul odors may indicate septic system malfunctions, while wet or soggy areas in the yard could suggest drain field failures. If you notice these signs in conjunction with visual cues in the diagram, it is crucial to take immediate action to prevent further damage and seek professional assistance for proper diagnosis and resolution.
By carefully analyzing the septic tank diagram and observing visual cues, homeowners can gain valuable insights into potential problems within their septic system. However, it is important to note that troubleshooting and problem diagnosis based on visual cues alone may not always provide a definitive diagnosis. In complex situations or when in doubt, it is best to consult with qualified septic system professionals who have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and address issues. Their expertise ensures proper solutions and prevents further damage to the septic tank system.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations for Septic Tank Systems
While the article mentions the CDC's requirement for septic systems to be at least fifty feet away from drinking water sources, there are other important regulatory considerations and environmental impacts associated with septic tank systems. Understanding these factors is crucial for homeowners to ensure compliance with regulations and minimize the environmental footprint of their septic systems. Let's explore some key points to consider:
1. Local Regulations
In addition to the CDC guidelines, it is essential to familiarize yourself with local regulations governing septic tank systems. Local health departments or environmental agencies often have specific requirements regarding system installation, maintenance, and even design. These regulations may include setback distances from property boundaries, restrictions on system size or type, and mandatory inspections. By adhering to local regulations, homeowners can avoid legal issues and contribute to the overall health and safety of their community.
2. Permits and Approvals
Depending on your location, obtaining permits and approvals may be necessary before installing or modifying a septic tank system. These permits ensure that the system meets the required standards and regulations. It is advisable to consult with local authorities or septic system professionals to determine the specific permits or approvals needed for your area. Failing to obtain the necessary permits can result in penalties or even the need to remove or alter the system.
3. Environmental Impact
Septic systems have the potential to impact the environment if not properly designed, installed, and maintained. Improperly treated wastewater can contaminate groundwater, surface water, and nearby bodies of water, leading to adverse effects on ecosystems and human health. It is crucial to ensure that your septic system is adequately sized for your household's needs, properly maintained, and regularly inspected to prevent leaks, overflows, and the release of untreated wastewater into the environment.
4. Water Conservation
Water conservation is not only important for reducing strain on the septic system but also for promoting sustainability and environmental responsibility. Conserving water through practices such as using efficient fixtures, repairing leaks promptly, and adopting responsible water usage habits can help prevent overloading the system, reduce the frequency of pumping, and minimize the environmental impact of the septic system.
5. Professional Inspections and Maintenance
Regular professional inspections and maintenance play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulations and minimizing environmental impact. Professional septic system inspections can identify potential issues, such as leaks or system failures, and address them promptly. Professionals can also advise on appropriate maintenance practices, including pumping schedules and proper waste disposal. By following professional guidance, homeowners can contribute to a healthy environment and a well-functioning septic system.
Understanding the regulatory requirements and environmental considerations associated with septic tank systems is essential for responsible homeownership. By complying with regulations, conserving water, and prioritizing proper maintenance, homeowners can minimize their environmental impact and ensure the long-term viability and efficiency of their septic systems. If you have any specific regulatory questions or concerns, it is advisable to consult with local authorities or septic system professionals for accurate and up-to-date information.
Septic System Design Variations
While the article briefly touches on septic system setups in suburban and rural areas, it is important to explore the various design variations that exist beyond these categories. Different types of septic systems are available to suit specific site conditions, soil types, and environmental considerations. Let's delve into some alternative designs, such as aerobic systems and mound systems, and discuss their unique features and requirements:
1. Aerobic Systems
 |
| Diagram of an Aerobic Septic System |
Aerobic systems typically consist of multiple compartments or chambers that facilitate the treatment process. They require a reliable source of electricity to power the aerator, which supplies the necessary oxygen. Aerobic systems are commonly used in areas with challenging soil conditions or where stricter effluent quality standards must be met. Regular maintenance, including inspections and the periodic addition of aerobic bacteria or disinfectants, is crucial for optimal performance.
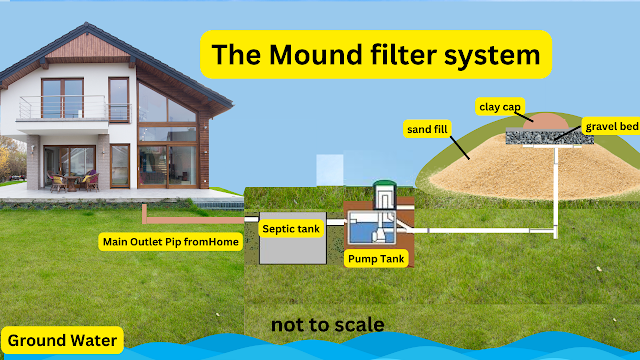
2. Mound Systems
Mound systems are designed for sites with soil conditions that are not suitable for conventional drain field installation, such as shallow bedrock, high groundwater tables, or poor draining soils. These systems involve the construction of an elevated mound or raised bed above the natural ground level to provide adequate treatment and disposal of effluent.
Mound systems typically consist of a gravel or sand bed with specially engineered fill material to create a raised area for effluent treatment. The effluent is evenly distributed over the mound through a network of perforated pipes or chambers. As the effluent passes through the mound, it is naturally filtered and treated by the soil before it reaches the groundwater.
Mound systems require careful design and construction to ensure proper functionality. Regular inspections and maintenance, such as monitoring the height of the mound, preventing surface water intrusion, and managing vegetation on the mound, are necessary to preserve their effectiveness.
3. Other Design Variations
Beyond aerobic systems and mound systems, there are additional design variations available for septic systems. Some examples include:
Drip Irrigation Systems: These systems utilize a network of small-diameter tubing or drip lines buried below the surface to distribute effluent slowly and uniformly to a large area. Drip irrigation systems are often used in areas with specific water reuse requirements or sites with limited space.
Chamber Systems: Chamber systems involve the use of lightweight plastic chambers instead of traditional gravel-filled trenches for effluent distribution. The chambers provide a larger surface area for effluent dispersal, enhancing treatment and reducing the overall footprint of the drain field.
Alternative Media Systems: Certain septic systems utilize alternative media, such as peat moss, coconut coir, or synthetic materials, in place of conventional gravel in the drain field. These media offer increased treatment capabilities and can be beneficial in areas with challenging soil conditions.
Each of these design variations has specific features, requirements, and maintenance considerations. It is important to consult with septic system professionals or regulatory authorities to determine which design is most suitable for your site conditions and environmental requirements. Proper installation, regular inspections, and adherence to maintenance protocols are essential to ensure the effective and sustainable operation of alternative septic system designs.
Hiring Professional Help for Your Septic System
While the article mentions consulting professionals for specific tasks like septic tank cleaning and inspections, it is important to understand when it's necessary to hire septic system professionals, the services they provide, and how to find reputable professionals in the field. Let's delve into these aspects to help you make informed decisions when seeking professional assistance for your septic system needs:
When to Hire Septic System Professionals
It is advisable to hire septic system professionals in the following situations:
Installation and System Design: When installing a new septic system or making significant modifications to an existing one, it is crucial to engage professionals who have expertise in septic system design and installation. They can assess site conditions, conduct soil tests, and develop a system that meets regulatory requirements and best practices.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Septic system professionals should be engaged for routine maintenance tasks such as septic tank pumping, inspections, and overall system evaluations. They have the knowledge and equipment to assess the condition of your system, identify potential issues, and recommend appropriate measures to maintain optimal functionality.
Repairs and Troubleshooting: If you encounter septic system problems such as backups, foul odors, or system malfunctions, it is advisable to hire professionals for repairs and troubleshooting. They can accurately diagnose the issue, recommend solutions, and perform repairs to restore the system's proper functioning.
Services Provided by Septic System Professionals
Septic system professionals offer a range of services, including:
System Installation and Design: Professionals can assess site conditions, perform soil tests, and design septic systems tailored to specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Professionals can conduct routine maintenance tasks, such as septic tank pumping or septic tank clean out, inspections, and assessments to ensure optimal system performance.
Repairs and Troubleshooting: Septic system professionals have the expertise to diagnose and address various system issues, including blockages, leaks, drain field failures, and component malfunctions.
System Upgrades and Modifications: If your septic system needs upgrades or modifications to meet changing needs or regulatory standards, professionals can guide you through the process and implement the necessary changes.
Finding Reputable Septic System Professionals
To find reputable septic system professionals, consider the following steps:
Research and Recommendations: Seek recommendations from friends, family, or neighbors who have recently engaged septic system professionals. Additionally, conduct online research, read reviews, and check professional directories to gather a list of reputable professionals in your area.
Licensing and Certification: Ensure that the professionals you consider hiring are licensed and certified in septic system installation, maintenance, or repair. Valid licensing and certification demonstrate their expertise and adherence to industry standards.
Experience and Expertise: Look for professionals with extensive experience in the septic system industry. Consider their track record, years of operation, and specific expertise in the services you require.
Obtain Multiple Quotes: Request quotes from several reputable professionals to compare prices, services offered, and warranties. This allows you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and budget.
Professional Associations: Consider professionals who are members of recognized industry associations, as they are likely to uphold high standards and stay updated on the latest practices in the field.
By following these steps, you can find reputable septic system professionals who can provide quality services and ensure the proper care and maintenance of your septic system.
Remember, proper maintenance, timely repairs, and professional guidance are key to ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and environmental soundness of your septic system.
Safety Precautions for Working with Septic Tanks
While the article mentions the hazards associated with septic tanks and filters, it is important to place greater emphasis on safety precautions when working with these components. Proper safety measures help prevent accidents, protect your health, and ensure the safe handling of wastewater, chemicals, and equipment. Here are some key safety precautions to consider:
Wear Protective Gear: When working with septic tanks or handling septic system components, always wear appropriate protective gear. This may include gloves, goggles, masks, coveralls, or rubber boots. Protective gear helps minimize the risk of direct contact with wastewater, chemicals, or pathogens present in the system.
Avoid Direct Contact with Wastewater: Septic tank wastewater can contain harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Avoid direct contact with wastewater by wearing protective gloves and ensuring that cuts or open wounds are covered with waterproof bandages. If contact occurs, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and clean water.
Handle Chemicals and Equipment Properly: Follow manufacturer instructions when handling chemicals used in septic systems, such as additives or cleaning agents. Store chemicals in a safe and secure location, away from children and pets. Additionally, handle equipment, such as pumps or tools, with caution, and ensure they are in good working condition to prevent accidents.
Proper Ventilation: When working in enclosed spaces, such as pump chambers or confined areas around the septic tank, ensure proper ventilation. Lack of ventilation can lead to the accumulation of harmful gases, such as methane or hydrogen sulfide. Open windows, use fans, or wear respiratory protection if necessary.
Prevent Falls and Physical Hazards: Be mindful of potential physical hazards around the septic tank, such as uneven surfaces, slippery areas, or tripping hazards. Use caution when accessing or inspecting the tank, and consider using safety barriers or warning signs to prevent accidents. Ensure that ladders or platforms used for access are sturdy and properly secured.
Follow Proper Waste Disposal Practices: When cleaning or maintaining septic tanks or filters, dispose of waste materials properly. Follow local regulations for the disposal of sludge, filter media, or other waste generated during maintenance activities. Improper disposal can have environmental implications and pose health risks.
Seek Professional Help When Needed: Some septic system maintenance tasks are best left to professionals. If you are uncertain or uncomfortable with a specific task, such as cleaning out the septic tank or working on electrical components, it is safer to seek professional help.
Remember, safety should always be a top priority when working with septic tanks. By following these safety precautions and exercising caution, you can protect yourself, prevent accidents, and ensure the safe and efficient maintenance of your septic system.
Upgrading or Replacing a Septic System
While the article briefly mentions the installation of a drain field and its importance, it is necessary to provide more information on upgrading or replacing septic systems. Understanding when it is necessary, available options, and the process involved can help homeowners make informed decisions about their septic system needs. Here's an overview of upgrading or replacing a septic system:
When is Upgrading or Replacement Necessary?
Upgrading or replacing a septic system may be necessary in the following situations:
System Failure: If your current septic system is experiencing frequent backups, foul odors, drain field failures, or other persistent issues that cannot be resolved through repairs, it may be time for an upgrade or replacement.
Regulatory Compliance: If there have been changes to local regulations or health department requirements since the installation of your septic system, an upgrade or replacement may be necessary to ensure compliance with the updated standards.
Increased Household Size or Water Usage: If your household has expanded, leading to increased water usage, or if you have made significant changes to your property, such as adding additional bathrooms or living units, an upgrade or replacement may be needed to accommodate the increased wastewater flow.
Environmental Considerations: If you are seeking to minimize the environmental impact of your septic system or if you live in an environmentally sensitive area, you may choose to upgrade to a more advanced system that provides enhanced treatment capabilities.
Available Options for Upgrading or Replacement
When considering upgrading or replacing a septic system, several options are available:
Conventional System: A conventional septic system consists of a septic tank for primary treatment of wastewater and a drain field for secondary treatment and disposal. Upgrading a conventional system may involve increasing the size of the tank, improving the drain field, or adding components such as filters or effluent pumps.
Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs): ATUs are advanced septic systems that provide enhanced treatment of wastewater by introducing oxygen into the treatment process. ATUs are suitable for challenging soil conditions, areas with strict effluent quality requirements, or those looking for environmentally friendly options.
Advanced Treatment Systems: Advanced treatment systems, such as sand filters, constructed wetlands, or recirculating media filters, offer higher levels of treatment than conventional systems. These systems can be used in areas with specific water reuse requirements, sites with poor soil conditions, or where a higher level of treatment is desired.
The Process of Upgrading or Replacement
The process of upgrading or replacing a septic system typically involves the following steps:
Assessment and Design: Engage a septic system professional to assess your current system and site conditions. They will evaluate the suitability of your existing system and recommend appropriate upgrades or replacement options based on your needs.
Permitting and Approvals: Obtain any necessary permits or approvals required by local health departments or regulatory authorities for the upgrade or replacement. Ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
System Installation: Once the design is finalized and permits are obtained, the installation process begins. This may include excavating and installing a new septic tank, drain field, or other system components as per the recommended design.
Inspections and Testing: Following installation, the septic system will undergo inspections and testing to ensure proper functionality and compliance with regulations. This may involve soil percolation tests, flow rate measurements, or other assessments.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: After the upgrade or replacement, adhere to regular maintenance schedules recommended by professionals. This may include routine inspections, pumping, and other maintenance tasks to keep the system in optimal condition.
It is essential to consult with septic system professionals throughout the upgrading or replacement process. They can provide expert guidance, design the system to meet your specific needs, and conduct the necessary inspections and testing. They will also provide information on proper maintenance procedures to ensure the longevity and efficient operation of the upgraded or replaced septic system.
Finding Reputable Professionals
When embarking on the process of upgrading or replacing your septic system, it is crucial to find reputable professionals who specialize in septic system installations and upgrades. Consider the following steps to find reliable experts:
Research and Recommendations: Seek recommendations from friends, neighbors, or local community groups who have recently undergone septic system upgrades or replacements. Conduct online research to identify professionals with positive reviews and a proven track record.
Licensing and Certification: Verify that the professionals you are considering are licensed and certified in septic system installation and maintenance. Valid licensing ensures that they have met the necessary requirements and possess the expertise to perform the job correctly.
Experience and Expertise: Look for professionals with extensive experience in septic system installations and upgrades. Inquire about their previous projects, particularly those similar to your specific needs. Experienced professionals are better equipped to handle challenges and deliver quality results.
Obtain Multiple Quotes: Request quotes from several reputable professionals. Compare the proposed scope of work, timelines, and pricing to make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and requirements.
Professional Associations: Consider professionals who are members of recognized industry associations, such as the National Onsite Wastewater Recycling Association (NOWRA) or state-level organizations. Membership in these associations demonstrates a commitment to industry standards and continuing education.
Remember to ask questions during the selection process. Inquire about their recommended upgrades or replacement options, warranties, and post-installation support. A reputable professional will be transparent, provide clear explanations, and offer ongoing assistance.
Final Thoughts
Upgrading or replacing a septic system is a significant investment that requires careful consideration and professional expertise. By understanding when an upgrade or replacement is necessary, exploring available options, and finding reputable professionals, you can ensure that your new septic system meets your needs, complies with regulations, and operates efficiently. Seek guidance from experienced professionals throughout the process to make informed decisions and achieve a well-functioning septic system that provides long-term benefits for your property and the environment.
Remember, every small action counts. By implementing conservation measures and making environmentally conscious choices, you can help protect water resources, preserve ecosystems, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Take an active role in the care and management of your septic system, and encourage others to do the same. Together, we can minimize the environmental impact of septic systems and ensure a healthier environment for future generations.
Research and fact Checked:
https://www.ukdpsolutions.co.uk/blog/tree-root-damage-to-a-septic-tank
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Septic_tank


.png)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment