Protect Your Health And Environment With Proper Septic System Care
 |
| Protect Your Health And Environment With Proper Septic System Care |
Introduction
Septic systems are an integral part of many residential and commercial properties, providing a safe and efficient means of managing wastewater. However, failing to properly maintain and care for these systems can result in serious health and environmental risks.
The release of harmful contaminants into the groundwater can lead to the pollution of bodies of water and damage to surrounding ecosystems, while the potential for diseases like dysentery, hepatitis, and typhoid fever can pose a risk to public health.
To avoid these risks and ensure the proper functioning of septic systems, regular maintenance and inspection are crucial. This article will explore the importance of proper septic system care and provide practical tips for protecting your health and the environment.
By understanding the components of septic systems, the potential health and environmental risks associated with their failure, and the steps required for proper maintenance and inspection, property owners can take proactive steps to protect themselves, their community, and the environment.
Key Takeaways
- Proper maintenance and inspection of septic systems are crucial for protecting public health and the environment.
- Regular pumping of septic tanks is important for removing accumulated solids and preventing system failure.
- Homeowners should avoid flushing non-biodegradable materials and using harsh chemicals that can kill good bacteria in the tank.
- Signs of septic system failure, such as slow draining sinks or toilets, sewage odors, and wet spots or standing water in the yard, should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage.
Septic System Components
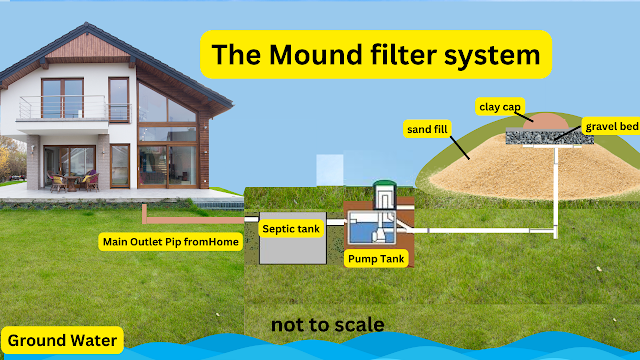
The septic system consists of two main components, a receiving tank and a leaching system, which work together to treat and dispose of wastewater.
The receiving tank is responsible for holding the wastewater until it can be treated by the good bacteria present in the tank. The tank is divided into two layers, the sludge layer on the bottom and the scum layer on top. The sludge layer is composed of the heavier solids that sink to the bottom, while the scum layer is made up of lighter solids that float to the top. The good bacteria present in the tank liquefy the waste and eliminate toxins, viruses, and bad bacteria.
The wastewater then passes through the leaching system, which is responsible for disposing of the treated wastewater into the soil. Leaching system design is essential in ensuring the proper function of the septic system. The leaching system is composed of a series of pipes that are placed in trenches filled with gravel and soil. The wastewater filters through the gravel and soil, where it is further treated and absorbed by the surrounding soil.
Proper maintenance of the tank and leaching system is crucial in ensuring the longevity of the septic system. Tank maintenance techniques include regular pumping of the tank to remove the sludge and scum layers that can accumulate over time, while leaching system maintenance includes avoiding the use of heavy machinery or construction on top of the leaching area.
Health and Environmental Risks
Failing septic systems can lead to the discharge of unsafe contaminants into groundwater and bodies of water, which can damage ecosystems and pose health risks such as dysentery, hepatitis, and typhoid fever. These contaminants can include nitrogen, phosphorus, and bacteria, which can cause harmful algal blooms, fish kills, and other negative impacts on aquatic life. In addition, groundwater contamination can lead to the spread of disease-causing microorganisms, which can pose a risk to public health.
To prevent dysentery and other health risks associated with failing septic systems, it is important to properly maintain and inspect these systems on a regular basis. This includes pumping the tank every 3-5 years, avoiding flushing non-biodegradable materials down the toilet, and avoiding the use of harsh chemicals that can kill the good bacteria in the tank. By taking these steps, homeowners can protect their health and the environment, while also ensuring that their septic system functions properly for years to come.
| Contaminant | Health Effects | Environmental Effects | | --- | --- | --- | | Nitrogen | Can cause methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) in infants | Can cause harmful algal blooms, fish kills, and other negative impacts on aquatic life | | Phosphorus | Can cause excessive plant growth and oxygen depletion in water bodies | Can cause harmful algal blooms, fish kills, and other negative impacts on aquatic life | | Bacteria | Can cause dysentery, hepatitis, and other illnesses | Can pose a risk to public health and harm aquatic life | | Nitrogen | Can contribute to eutrophication and harmful algal blooms | Can lead to oxygen depletion and negative impacts on aquatic life and water quality |
Proper Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of septic systems is crucial for ensuring their proper function and preventing the discharge of harmful contaminants into groundwater and bodies of water.
Septic system pumping is an important aspect of maintenance, as it involves removing the accumulated solids from the tank before they can build up and cause problems. The frequency of pumping depends on several factors, such as the size of the tank, the number of people using the system, and the amount of wastewater generated. Generally, it is recommended to pump the tank every three to five years, but this may vary depending on individual circumstances. Neglecting to pump the tank can lead to the accumulation of solids and scum, which can cause blockages and backups in the system, resulting in wastewater backup in the house or yard.
In addition to pumping, regular inspections are necessary to identify any signs of septic system failure. Signs of a failing system may include slow draining sinks or toilets, sewage odors inside or outside the home, gurgling sounds in the plumbing, and wet spots or standing water in the yard. Inspections can also identify any damage to the tank or leaching system, such as cracks, leaks, or clogs. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and ensure the continued proper function of the system.
Overall, proper maintenance and inspection of septic systems are essential for protecting public health and the environment by minimizing harmful contaminants and pollutants.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should a septic system be pumped?
Septic system maintenance requires pumping the tank every 3-5 years to remove accumulated sludge and scum layers. Signs of a full tank include slow drainage, sewage backups, and odors. Neglecting pumping can lead to system failure and environmental pollution.
Can household cleaners affect the function of a septic system?
Household cleaners can have a chemical impact on septic systems by killing the good bacteria necessary for waste breakdown. Eco-friendly alternatives, such as vinegar and baking soda, are recommended to maintain proper system function.
What should be done if a septic system alarm goes off?
If a septic system alarm goes off, immediate troubleshooting is necessary to prevent septic tank overflow. Check the breaker, pump, and float switch. If the issue persists, seek professional help for emergency response and maintenance.
Output for discussion ideas:
Septic system regulations, environmental impact assessment.
Can the use of a garbage disposal impact the health of a septic system?
The use of a garbage disposal can impact the health of a septic system by increasing the amount of solid waste and reducing the number of septic tank bacteria. Garbage disposal maintenance, including regular pumping and avoiding certain food waste, can help mitigate these effects.
Are there any septic system additives that can improve its function?
Septic system additives are marketed to improve system function, however, their effectiveness concerns are still unknown. Eco-friendly options, such as using natural bacteria, have shown promising results, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proper septic system care is crucial for protecting both public health and the environment. Failing septic systems can release harmful contaminants into the groundwater, leading to pollution of bodies of water and damage to ecosystems. In addition, these systems can pose a risk to public health, with the potential for diseases like dysentery, hepatitis, and typhoid fever.
To ensure the proper function of septic systems, regular maintenance and inspection are essential. This includes regular pumping, avoiding flushing harmful materials down the drain, and ensuring proper drainage and ventilation.
By following these guidelines, individuals can help protect their health and the environment, while also ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of their septic systems. It is important for individuals to take responsibility for the proper care of their septic systems, as it has a significant impact on both public health and the environment.
Research and Fact checked:


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment