From Clay To Sand: Understanding Soil Types And Their Impact On Your Septic System
 |
| Soil Types And Their Impact On Your Septic System |
Are you considering installing a septic system on your property? Before you make any decisions, it's crucial to understand the impact that soil types can have on the functionality and long-term success of your system.
In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of clay and sandy soils, examining their properties and how they can potentially affect your septic system.
Clay soil is known for its fine particles and ability to retain water. This type of soil has low permeability, meaning it doesn't allow water to pass through easily. While this may seem like a good thing for a septic system, as it could prevent wastewater from leaching into surrounding areas too quickly, there are challenges that come with clay soil. Its compact nature can lead to poor drainage and slower absorption rates, which in turn can cause effluent backup or surfacing issues if not properly managed. Understanding these challenges is essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your septic system in clay soil conditions.
On the other hand, sandy soil has larger particles and high permeability, allowing water to move through more readily. This type of soil drains quickly but also poses potential issues for septic systems. The fast drainage rate may result in inadequate treatment time for wastewater before it reaches groundwater sources or nearby surface water bodies. Additionally, sandy soil's lack of cohesive structure may pose challenges when it comes to distributing effluent evenly across the drainfield area. By comprehending these factors associated with sandy soils, homeowners can make informed decisions about their septic systems.
In conclusion, understanding the characteristics of different soil types is crucial when considering a septic system installation or maintenance plan. Whether you're dealing with clay or sandy soil on your property, being aware of their unique properties will help you address potential challenges effectively and make informed decisions regarding design modifications or alternative systems if necessary.
Stay tuned as we dive deeper into each type of soil's impact on septic systems and explore strategies to overcome any obstacles that may arise.
Characteristics of Clay Soil
Clay soil, with its dense and sticky texture, poses unique challenges for septic systems. Understanding the composition of clay soil is crucial in order to design an efficient and effective septic system.
Clay soil is primarily composed of fine particles that are easily compacted, leading to poor drainage and potential issues with the septic system. Due to its compact nature, water has difficulty infiltrating through clay soil, resulting in slow percolation rates and a higher risk of clogging.
The composition of clay soil plays a significant role in its behavior. It contains high amounts of colloidal particles that have a strong affinity for water molecules. This causes the soil to retain water for longer periods, making it difficult for excess moisture from the septic system to drain away properly. Additionally, clay soils have small pore spaces between particles, limiting the movement of air and water within the soil profile.
Compaction is another critical aspect when dealing with clay soil and septic systems. The weight of heavy equipment during installation or maintenance can compress the already dense clay particles even further. This compaction reduces permeability and increases the risk of effluent backup or ponding around the drain field area.
Understanding these characteristics of clay soil helps in designing appropriate measures to overcome its limitations while ensuring proper functioning of septic systems. Proper site evaluation, including thorough percolation tests specific to clay soils, should be conducted prior to installing a septic system on such sites. Taking into account factors such as adequate separation distances from groundwater sources and implementing additional drainage measures like mounding or adding sand layers can help mitigate some challenges posed by this type of soil composition. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections of the septic system can ensure its proper functioning and prevent potential issues caused by the soil composition.
Challenges with Clay Soil and Septic Systems
Despite its challenges, clay soil can pose difficulties for septic systems. The composition of clay soil plays a significant role in these challenges. Clay soil is composed of very fine particles that have the tendency to compact tightly together, creating dense and impermeable layers. This compaction restricts the movement of water through the soil, making it difficult for effluent from a septic system to properly drain and be filtered.
Furthermore, clay soil has a high water-holding capacity, which means it can retain large amounts of moisture. This can lead to saturation of the soil, causing further problems for septic systems. When clay becomes saturated with water, it becomes even more impermeable, preventing proper drainage and filtration.
As a result, effluent from the septic system may not adequately disperse into the surrounding soil and could potentially accumulate on the surface or back up into the house.
Understanding the challenges posed by clay soil is crucial when considering its impact on septic systems. The composition of clay soil makes it susceptible to compaction and poor drainage, which can hinder the proper functioning of a septic system. Taking appropriate measures such as regular maintenance and possibly implementing alternative drainage methods can help mitigate these challenges and ensure optimal performance of your septic system in areas with clay soil composition.
Properties of Sandy Soil
With its loose texture and ability to drain water quickly, sandy soil brings a light and airy feel to any landscape. Sandy soil is characterized by its large particles, which allow for excellent drainage and aeration.
This type of soil is known for its drought resistance, as it doesn't retain moisture well and allows excess water to easily flow through. Due to its fast-draining nature, sandy soil requires frequent irrigation during dry periods to maintain proper moisture levels for plant growth.
In terms of fertility management, sandy soil poses some challenges. The loose structure of this soil type allows nutrients to leach out quickly, making it necessary for regular fertilization to ensure optimal plant health. Additionally, sandy soils tend to have low organic matter content, which further reduces their nutrient-holding capacity.
To enhance fertility in sandy soil, organic amendments such as compost or well-rotted manure can be incorporated to improve nutrient retention and overall soil quality.
Overall, sandy soil offers good drainage properties and drought resistance, but it requires careful attention when it comes to maintaining fertility levels. By implementing appropriate fertilization practices and incorporating organic matter into the soil, you can maximize the productivity of your landscape despite the challenges posed by this unique soil type.
Potential Issues with Sandy Soil and Septic Systems
When dealing with sandy soil, you'll want to be aware of any potential issues that may arise with your septic system. Sandy soil composition can present unique challenges for septic system maintenance.
One of the main concerns is the rapid drainage properties of sandy soil. While this allows for efficient movement of water through the soil, it also means that solids in the wastewater can easily pass through and reach groundwater sources without proper treatment.
To address this issue, regular septic system maintenance becomes crucial when dealing with sandy soil. It is important to monitor and pump the tank more frequently compared to other types of soil. This ensures that solids are removed before they have a chance to clog or damage the drainage field. Additionally, using effluent filters can help trap smaller particles and prevent them from entering the drainfield.
Furthermore, due to its fast-draining nature, sandy soil may not provide sufficient filtration or treatment of wastewater contaminants. To mitigate this risk, installing an additional layer of specialized filter media such as peat moss or synthetic fabrics can enhance treatment capabilities before effluent reaches groundwater sources.
Overall, understanding the characteristics of sandy soil composition and taking appropriate measures for septic system maintenance are essential for long-term functionality and environmental protection. By staying vigilant and implementing necessary precautions, you can ensure that your septic system operates effectively even in areas with sandy soils, high water tables, or other challenging conditions.
Making Informed Decisions for Your Septic System
To ensure the long-term functionality and environmental protection of your septic system, it's crucial to make informed decisions based on your specific needs and circumstances.
One important aspect of maintaining a septic system is regular maintenance. This includes pumping out the tank every few years to remove accumulated solids and prevent clogs or backups. Additionally, inspecting the system for any signs of leakage or damage is essential in order to address issues before they become major problems.
Another key factor in making informed decisions for your septic system is soil testing. Understanding the type of soil in your area can greatly impact the design and performance of your septic system. Different soils have varying levels of permeability, which affects how quickly water can move through them. For example, sandy soil has high permeability, meaning that water flows through it easily. This can result in faster drainage from the septic system, but also increases the risk of contaminants reaching groundwater sources.
By conducting soil testing, you can determine whether additional measures are needed to optimize your septic system's performance based on your specific soil conditions. This may include installing a larger drainfield or using alternative treatment technologies to ensure proper treatment of wastewater before it reaches the ground.
Consulting with a professional who specializes in septic systems can provide valuable insights into making informed decisions that'll help protect both your investment and the environment for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How deep should my septic system be installed in clay soil?
For clay soil compaction, it is recommended to install the septic system at a depth of at least 3 feet. This depth ensures sufficient separation from the soil surface and allows for proper functioning of the system.
Can clay soil be improved for better septic system performance?
To improve clay soil for better septic system performance, you can add organic matter like compost or peat moss to increase drainage and enhance soil structure. This will help prevent clogging and ensure proper wastewater treatment.
Are there any specific septic system designs that work well with clay soil?
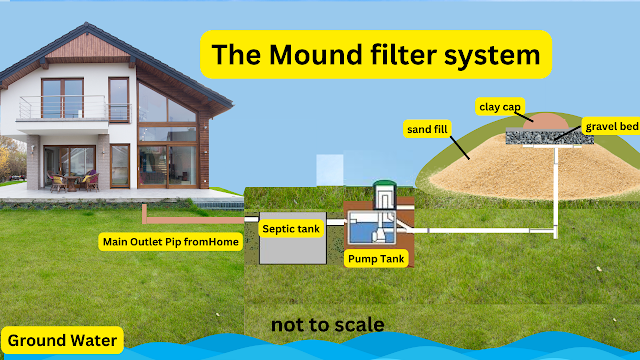
Specific septic designs that work well with clay soil include mound systems, raised bed systems, and pressure distribution systems. These designs help overcome the challenges of clay soil compatibility by providing proper drainage and preventing system failure.
How often should clay soil be inspected for septic system maintenance?
Clay soil should be inspected regularly for septic system maintenance due to its specific characteristics. The frequency of inspections depends on the soil composition and its impact on the septic system's functionality, making it crucial for proper maintenance.
Can sandy soil be used as a natural filter for septic system effluent?
Sandy soil can serve as a natural filter for septic system effluent, improving septic system efficiency. The porous nature of sandy soil allows for better filtration and drainage, reducing the risk of contamination.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the characteristics of different soil types is crucial when it comes to selecting and maintaining a septic system.
Clay soil, with its fine particles and high water holding capacity, poses challenges such as slow drainage and potential clogging of drain fields. On the other hand, sandy soil, with its coarse texture and good drainage properties, may lead to quicker wastewater movement but can also result in excessive leaching and nutrient loss.
When making decisions for your septic system, it's essential to consider the specific soil type on your property. Conducting thorough soil testing will provide valuable information about its composition and suitability for a septic system installation. Consulting with professionals who specialize in septic systems can help you navigate through these complexities and make informed choices regarding design modifications or maintenance strategies.
To ensure the long-term functionality of your septic system, regular monitoring and proper maintenance practices are vital regardless of the soil type. This includes regular pumping of the tank, avoiding excessive water usage or disposal of non-biodegradable materials into the system.
By understanding how clay or sandy soils interact with septic systems, homeowners can take proactive measures to prevent issues before they occur and extend the lifespan of their septic systems while protecting their property's value.
.png)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment