Septic System Innovations and Future Trends
Septic System Innovations and Future Trends: Discussing Upcoming Technological Advancements and Research Surrounding Septic Systems
Introduction
Septic systems play a crucial role in managing household wastewater in areas not connected to public sewage systems. These decentralized systems have been in use for decades, but with advancements in technology and growing environmental concerns, researchers and innovators are continuously working to enhance their efficiency and sustainability. In this article, we will explore the latest innovations and future trends in septic systems, shedding light on the potential technological advancements that aim to revolutionize the way we handle and treat wastewater.
1. Efficient Wastewater Treatment through Advanced Aerobic Systems
One of the most significant breakthroughs in septic system innovations is the development of advanced aerobic treatment units (ATUs). Unlike traditional anaerobic septic tanks, ATUs introduce oxygen into the treatment process, enhancing the breakdown of organic matter and reducing the release of harmful pathogens into the environment. These systems employ mechanisms such as diffusers, bubbling systems, and extended aeration to promote aerobic digestion, resulting in cleaner effluent.
Research indicates that ATUs exhibit better removal rates for nitrogen and other contaminants compared to conventional septic systems. Moreover, these systems have the potential to be smaller in size, making them suitable for installation in areas with limited space. As ongoing research continues to optimize ATU performance, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of this technology in the future.
2. SensorBased Monitoring and Maintenance
Monitoring and maintaining a septic system is crucial to prevent failures and ensure efficient operation. In the past, homeowners relied on predetermined schedules for pumpouts and inspections, which were often inefficient and prone to overlooking potential issues. However, recent advancements in sensor technology have introduced the concept of realtime monitoring and maintenance.
By employing pH sensors, pressure sensors, and flow meters, septic system owners can remotely monitor the status and performance of their systems. Realtime data allows for proactive measures, such as detecting leaks, abnormal microbial activity, or excessive water usage, before they turn into costly problems. Through continuous monitoring, homeowners can optimize system performance, prolong its lifespan, and reduce the likelihood of environmental contamination.
3. Innovative Materials and Design
The materials and design of septic systems are also evolving to address issues such as longevity, environmental compatibility, and costeffectiveness. Traditional septic tanks are typically made of concrete or steel, which can undergo degradation over time due to chemical reactions, internal bacterial growth, and ground movement. However, emerging materials, such as fiberglassreinforced plastic (FRP) and polyethylene, offer enhanced durability while remaining resistant to corrosion and structural damage.
Moreover, innovative septic system designs are being developed to cater to specific environmental conditions. For example, areas prone to flooding can benefit from elevated septic systems that prevent wastewater discharge during heavy rains, minimizing the risk of contamination. These advancements in materials and design aim to increase the lifespan of septic systems and reduce the maintenance and replacement costs for homeowners.
4. Integration of Renewable Energy
As the world moves towards sustainable practices, septic systems are also undergoing transformative changes to align with renewable energy sources. Researchers are exploring the integration of solar panels and smallscale wind turbines to power septic system components. By harnessing clean energy, septic systems can become more independent and reduce their environmental footprint.
Solarpowered septic systems have the potential to run the aeration units, pumps, and monitoring equipment, eliminating the need for gridbased electricity. This not only reduces the reliance on fossil fuels but also lowers operational costs for homeowners in the long run. As renewable energy technologies continue to advance, septic systems can play a part in the global transition toward a more sustainable future.
5. Nutrient Recovery and Reuse
Traditional septic systems primarily focus on wastewater treatment, but recent research has identified an opportunity to recover valuable nutrients from the effluent. Nutrient recovery technologies, including phosphorus and nitrogen extraction, offer the potential to transform septic systems into nutrientrecycling hubs. These recovered nutrients can be repurposed as fertilizers or used in other industries, reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers while minimizing environmental impacts.
By incorporating nutrient recovery into septic system designs, we can turn wastewater treatment into a resource recovery process, closing the loop on nutrient cycles. This innovation not only has ecological benefits but also presents economic opportunities for farmers and industries looking for sustainable alternatives.
Conclusion
Innovation and research in the septic system industry are paving the way for a greener and more efficient future. From advanced aerobic systems to sensorbased monitoring, innovative materials, renewable energy integration, and nutrient recovery, the future of septic systems is promising. As homeowners and environmentalists continue to prioritize water and soil conservation, investing in these future trends will prove instrumental in creating sustainable wastewater management systems.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts on septic system innovations and future trends in the comments below. Let us know your experiences and any additional insights you may have. Together, we can drive the advancement of septic system technologies and promote responsible wastewater management.
Meta Tag Keywords



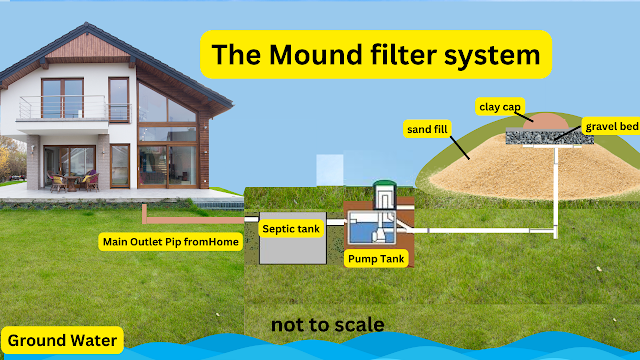
.png)





Comments
Post a Comment