Exploring Septic Systems in Rural Areas: How Do They Work?
 |
| Septic Systems in Rural Areas: How Do They Work |
Are you ready to dive deep into the inner workings of septic systems in rural areas? Brace yourself for a journey of knowledge as we unravel the mysteries behind these underground giants.
In this article, we will explore the intricate mechanisms that keep
your septic tank running smoothly and efficiently. From waste collection to
treatment and disposal, we will guide you through every step, equipping you
with the knowledge to maintain a healthy septic system in your rural setting.
Let's embark on this enlightening adventure together.
Key Takeaways
•
Septic tanks are underground
containers that collect and treat wastewater in rural areas.
•
The components of a septic
system include the septic tank, drainfield, distribution box, and soil.
•
The process of waste treatment
involves separating solids, treating effluent in the drainfield, and filtering
through soil.
•
Regular maintenance,
inspections, and proper waste disposal are crucial for the proper functioning
of septic systems in rural areas.
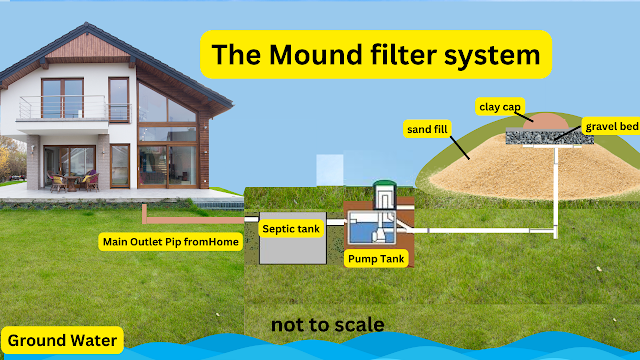
The Role of a
Septic Tank in Rural Areas
In
rural areas, your septic tank plays a crucial role in the proper disposal of
wastewater. A septic tank is a large underground container made of concrete,
fiberglass, or plastic. Its purpose is to collect and treat the wastewater
generated from your household.
When
you flush the toilet, take a shower, or use the sink, the wastewater flows into
the septic tank through pipes. Inside the tank, solid waste settles at the
bottom, while oils and fats float to the top. Bacteria present in the tank
break down the solid waste, turning it into sludge.
The
treated wastewater then flows out of the tank into the drain field, where it's
further treated by the soil. Regular maintenance of your septic tank is
essential to ensure its proper functioning and prevent any potential issues.
Understanding
the Components of a Septic System
To
understand how a septic system functions, you must be familiar with its main
components. Here are the four key elements that make up a septic system:
1.
Septic Tank: This is the
primary component of the system and is responsible for separating solids from
liquids. It holds the wastewater long enough for the solids to settle to the
bottom and the oils and grease to float to the top.
2.
Drainfield: Also known as a
leachfield, this is where the treated wastewater is dispersed into the soil.
The drainfield consists of a network of perforated pipes buried in trenches,
allowing the water to gradually seep into the ground.
3.
Distribution Box: The
distribution box evenly distributes the wastewater from the septic tank to the
drainfield. It ensures that the effluent is distributed evenly across the
entire drainfield area.
4.
Soil: The soil acts as the
final treatment and filtration system for the wastewater. It naturally filters
out any remaining contaminants, allowing the water to safely return to the
groundwater.
Understanding
these components of a septic system is crucial for its proper functioning and
maintenance.
The Process of
Waste Treatment in a Septic System
You
can understand how waste is treated in a septic system by learning about the
process.
The
process of waste treatment in a septic system begins with the collection of
wastewater from your household. This wastewater, which consists of everything
that goes down your drains and toilets, enters the septic tank.
Inside
the tank, the solid waste settles to the bottom, forming a layer of sludge,
while the lighter materials, like oils and grease, float to the top, creating a
layer of scum.
The
remaining liquid, known as effluent, flows out of the tank and into the
drainfield. In the drainfield, the effluent is further treated by the soil,
which acts as a natural filter, removing harmful bacteria and other
contaminants.
This
process ensures that the wastewater is properly treated and returned to the
environment safely.
Maintaining and
Caring for Your Septic System in a Rural Setting
Regular
maintenance and care are essential for keeping your septic system in good
working condition, especially in a rural setting where access to municipal
sewer systems may be limited. Here are four important aspects of septic tank
maintenance to consider:
1.
Pumping: Regularly schedule
septic tank pumping to remove accumulated sludge and prevent clogs or backups.
2.
Inspections: Conduct routine
inspections to check for any signs of leaks, cracks, or damage to the tank or
drain field.
3.
Water Usage: Be mindful of your
water usage to prevent overwhelming the septic system. Water conservation
measures, such as fixing leaks and using efficient appliances, can help.
4.
Proper Waste Disposal: Avoid
flushing non-biodegradable items, excessive chemicals, or large amounts of
grease down the drain. These can clog the system and hinder its performance.
Common Issues
and Troubleshooting for Rural Septic Systems
If
you notice strange odors coming from your septic system in a rural area, it
could be a sign of a potential issue that needs troubleshooting. Rural septic
systems face common issues that require attention to ensure proper functioning.
One
common problem is clogged pipes caused by the buildup of solid waste or tree
roots infiltrating the system. To troubleshoot this, you can use a plumbing
snake to clear any obstructions or hire a professional to perform a thorough
inspection.
Another
issue is a malfunctioning drain field, which can lead to wastewater backup and
pooling. To address this, you may need to have the drain field repaired or
replaced.
It's
essential to regularly inspect and pump your septic tank to prevent issues such
as overflows and leaks.
If
you encounter any problems beyond your expertise, it's recommended to consult a
septic system professional for assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should
a Septic Tank Be Pumped in a Rural Area?
In a rural area, a septic tank should be pumped every 3 to 5 years.
Regular pumping is crucial to prevent overflow and maintain the system's
efficiency. It's important to schedule this maintenance to avoid costly
repairs.
Can a Septic
System in a Rural Area Be Expanded or Upgraded if Needed?
Yes, a septic system in a rural area can be expanded or upgraded if
needed. You may need to consult with a professional to assess the feasibility
and requirements for such modifications.
Are There Any
Alternative Options to Septic Systems in Rural Areas?
There are alternative options to septic systems in rural areas.
These may include composting toilets, greywater systems, or connecting to a
nearby municipal sewer system if available. Consider the specific needs and
regulations of your area.
What Are the
Potential Health Risks Associated With a Failing Septic System in a Rural Area?
The potential health risks of a failing septic system in a rural
area include groundwater contamination, which can lead to the spread of
diseases such as hepatitis A and E. Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent
these risks.
Are There Any
Government Regulations or Guidelines for Septic Systems in Rural Areas?
Yes, there are government regulations and guidelines for septic
systems in rural areas. These rules ensure proper installation, regular
maintenance, and environmental protection. It is important to comply with these
regulations to avoid penalties and safeguard public health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, septic systems
play a crucial role in rural areas by effectively treating and disposing of
wastewater.
By understanding the components
and processes involved, you can ensure the efficient operation of your septic
system.
Remember, regular maintenance
and care are essential to avoid common issues.
As the saying goes, 'An ounce
of prevention is worth a pound of cure.'
So, take the necessary steps
to keep your septic system functioning smoothly and enjoy a clean and healthy
environment in your rural community.


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment