The Mechanics of Mound Septic Systems: How Do They Work?
 |
| Mound Septic Systems: How Do They Work |
Are you itching to unravel the mystery behind mound septic systems? Look no further! This article is your ultimate guide.
Mound septic systems are the go-to solution in areas with tricky
soil or high water tables. We'll break down the inner workings of these
marvels, explaining how they elevate the drain field above ground level for
optimal waste treatment.
With a second-person perspective, we'll navigate you through the
mechanics of mound septic systems, ensuring you gain a crystal-clear
understanding.
Let's embark on this enlightening journey together!
Key Takeaways
•
Mound septic systems have three
main components: septic tank, dosing chamber, and the mound or raised drain
field.
•
The septic tank separates solid
and liquid waste, capturing solids to prevent drain field clogs.
•
The dosing chamber evenly
distributes liquid waste to the drain field through multiple outlets equipped
with baffles or weirs.
•
The mound or raised drain field
filters and treats wastewater using layers of gravel, sand, and soil to remove
impurities and reduce contamination risks.
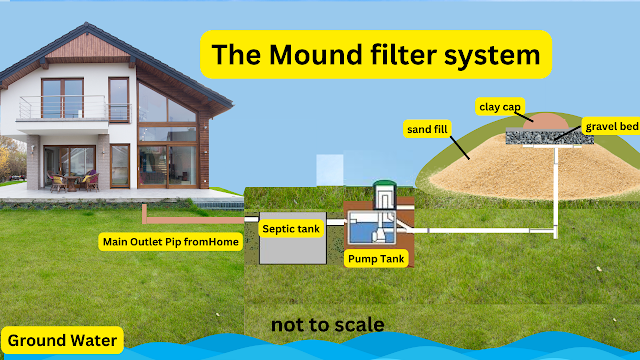
The Components of
a Mound Septic System
In
a mound septic system, you'll find three main components: a septic tank, a
dosing chamber, and a mound or raised drain field.
The
septic tank is where the wastewater from your home goes first. It separates the
solid waste from the liquid waste, allowing the solid waste to settle at the
bottom and the liquid waste to flow into the dosing chamber.
The
dosing chamber is responsible for evenly distributing the liquid waste to the
mound or raised drain field. This field is built above ground level to ensure
proper filtration and treatment of the wastewater.
The
mound or raised drain field consists of layers of gravel, sand, and soil, which
help to remove impurities and pathogens from the wastewater before it returns
to the environment.
Site Evaluation
and Design Considerations
To
ensure proper functionality of your mound septic system, it's important to
carefully evaluate the site and consider various design factors. Here are some
key considerations:
Site
Evaluation: - Determine the soil type and its ability to absorb and treat
wastewater. - Assess the groundwater level to ensure it's below the proposed
drain field elevation. - Evaluate the slope of the site to ensure proper
drainage.
Design
Factors: - Size the septic tank appropriately based on the number of occupants
and estimated wastewater flow. - Consider the size and configuration of the
mound to accommodate the required drain field area. - Determine the appropriate
height of the mound to raise the drain field above the groundwater level.
Construction and
Installation Process
You'll
begin the construction and installation process of your mound septic system by
preparing the site and excavating the area for the septic tank and drain field.
First,
ensure that the chosen location meets all necessary setback requirements. Once
the site is selected, mark the boundaries for the mound and mark the location
for the septic tank and drain field.
Use
a backhoe or excavator to dig a hole for the septic tank, making sure to follow
the manufacturer's specifications for dimensions and depth. Next, excavate the
area for the drain field, ensuring proper slope for wastewater flow.
Install
the septic tank according to the manufacturer's instructions and connect it to
the drain field. Finally, fill the area around the septic tank and drain field
with suitable fill material, compacting it in layers to create the mound.
Understanding the
Function of the Septic Tank
Your
understanding of the function of the septic tank is crucial for knowing how the
mound septic system operates effectively.
The
septic tank is the primary component of the system, responsible for the initial
treatment of wastewater. Here's a breakdown of its role in the mound septic
system:
•
The septic tank receives
wastewater from your house and separates it into three layers: solids, liquids,
and scum.
•
Solids settle at the bottom and
form sludge, while scum floats at the top.
•
Liquids, known as effluent, are
discharged into the drain field for further treatment.
The
septic tank's main function is to capture and hold solids, allowing them to
decompose over time. This prevents them from clogging the drain field and
ensures proper effluent distribution.
Understanding
the septic tank's role is essential for maintaining the functionality of the
mound septic system and preventing issues such as clogs and backups.
The Role of the
Distribution Box in Mound Systems
The
distribution box plays a vital role in the functionality of mound septic
systems by evenly distributing effluent to the drain field. This component is
typically made of concrete or plastic and is located between the septic tank
and the drain field.
Its
purpose is to collect and distribute the effluent from the septic tank to the
drain field pipes in a controlled and evenly distributed manner. The
distribution box contains multiple outlets or distribution lines that connect
to the drain field pipes. These outlets are equipped with baffles or weirs to
regulate the flow of effluent and ensure equal distribution across the drain
field.
How Effluent Is
Treated in Mound Systems
Effluent
in mound systems is treated through a process that involves aerobic bacteria
breaking down organic matter in the drain field. This treatment method ensures
that the wastewater is properly treated before being released into the
environment. Here is a deeper look into how this process works:
•
First, the effluent is
distributed evenly across the drain field. This helps to prevent any overload
on specific areas and promotes even treatment.
•
Once the effluent reaches the
drain field, the aerobic bacteria start their work. These bacteria thrive in
oxygen-rich environments and are responsible for breaking down the organic
matter present in the wastewater.
•
As the bacteria break down the
organic matter, they convert it into simpler compounds, such as carbon dioxide
and water. This process helps to remove harmful substances and pathogens from
the effluent.
•
The treated effluent then
percolates through the mound system's sand fill, which acts as a natural
filter, further removing any remaining impurities.
•
Finally, the treated effluent
is discharged into the surrounding soil, where it undergoes further filtration
and purification before entering the groundwater system.
Maintaining and
Monitoring Mound Septic Systems
To
ensure the optimal functioning of your mound septic system, it's crucial to
implement regular maintenance and monitoring practices.
This
includes scheduling routine inspections by a qualified professional to assess
the condition of the system and identify any potential issues.
Additionally,
it's important to be aware of signs of system failure, such as unpleasant
odors, slow drains, or pooling water, as these may indicate the need for
immediate attention to prevent further damage.
Cost of Maintenance
Maintaining a mound
septic system can be costly, as regular inspections and pump-outs are necessary
to ensure its functionality. Here are some key points to consider regarding the
cost of maintenance:
•
Regular inspections: These are
essential to identify any potential issues or malfunctions in the system. They
help in detecting problems at an early stage, which can save you from expensive
repairs or replacements in the future.
•
Inspection frequency: Depending
on the size of the system and local regulations, inspections may be required every
1-3 years.
•
Inspection costs: Typically, a
professional inspection can range from $200 to $500, depending on various
factors such as location and complexity of the system.
Pump-outs: Mound
septic systems require periodic pump-outs to remove accumulated solids and prevent
clogging of the drain field.
•
Pump-out frequency: On average,
pump-outs are recommended every 3-5 years, but this can vary depending on
household size and water usage.
•
Pump-out costs: The cost of a
pump-out can range from $200 to $600, depending on the size of the system and
the distance to the disposal site.
Considering these
factors, it's important to budget for regular maintenance to keep your mound
septic system functioning properly and avoid more significant expenses down the
line.
Inspection Frequency
Requirements
To
ensure the proper functioning of your mound septic system, it's important to
adhere to the required inspection frequency, which may vary depending on the
size of your system and local regulations.
Regular
inspections are necessary to identify any potential issues or malfunctions that
may compromise the performance of your system. During these inspections, a
trained professional will assess the condition of the mound, including the
integrity of the liner, the distribution pipes, and the pump chamber. They'll
also check for any signs of leaks or blockages that could affect the system's
efficiency.
Additionally,
inspections will ensure that the system is properly sized and functioning in
accordance with local regulations. By following the recommended inspection
frequency, you can proactively address any problems and ensure the long-term
functionality of your mound septic system.
Signs of System Failure
If you notice
foul odors, slow drainage, or sewage backups in your home, it could be a sign
that your mound septic system is failing. To understand the deeper meaning
behind these signs of system failure, consider the following:
•
Blocked distribution pipes:
When distribution pipes become clogged with solid waste or debris, it can cause
backups and slow drainage, leading to foul odors and potential system failure.
•
Leaking or damaged septic tank:
A leaking or damaged septic tank can allow untreated sewage to escape, causing
foul odors and potential contamination of surrounding soil and water sources.
These signs
indicate potential issues with your mound septic system and shouldn't be
ignored. It's important to address these problems promptly to prevent further
damage and ensure the proper functioning of your septic system. Regular
maintenance and inspection can help identify and resolve these issues before
they escalate.
Common Issues and
Troubleshooting Tips
If
you encounter issues with your mound septic system, there are several common
problems that may arise.
One
common issue is drain field saturation, which can occur when the system is
overloaded with wastewater and the soil is unable to properly absorb it.
Another
potential problem is pump failure, which can lead to backups and disruptions in
the system's functionality.
Finally,
system odors can be a common complaint, often caused by a lack of proper
ventilation or a buildup of waste materials.
Understanding
these common issues and utilizing troubleshooting tips can help you address and
resolve problems with your mound septic system.
Drain Field Saturation
When the drain
field of a mound septic system becomes saturated, it can lead to sewage backups
and potential health hazards. To understand this issue more deeply, consider
the following:
•
Factors that contribute to
drain field saturation:
•
Excessive rainfall or flooding:
When the soil becomes oversaturated with water, it hampers the absorption of
effluent in the drain field.
•
Poor soil percolation: If the
soil has a high clay content or lacks adequate drainage, it can lead to
saturation issues.
•
Consequences of drain field
saturation:
•
Sewage backups: When the drain
field is unable to absorb the wastewater properly, it can cause sewage to back
up into the house or yard.
•
Health hazards: Raw sewage
contains harmful pathogens that can pose serious health risks if exposed to
humans or animals.
It is crucial to
address drain field saturation promptly to prevent these detrimental
consequences. Regular maintenance, such as monitoring water usage and diverting
excess water away from the drain field, can help mitigate this issue.
Pump Failure Prevention
To prevent pump
failure in your mound septic system, regular maintenance and inspections are
essential.
The pump is a
vital component of the system, responsible for moving the effluent from the
septic tank to the drain field. Over time, pumps can become clogged or worn
out, leading to reduced efficiency or complete failure.
Regular
inspections allow you to identify any potential issues early on and take the
necessary steps to prevent further damage. During these inspections, it's
crucial to check the pump for any signs of wear, such as leaks or unusual
noises.
Additionally,
maintaining the pump by cleaning the filters and ensuring proper lubrication
can help extend its lifespan.
Alleviating System Odors
When it comes to
alleviating system odors in your septic system, there are a few key strategies
that can be employed. By following these methods, you can effectively eliminate
unpleasant smells and maintain a healthy environment.
Here are some
steps you can take:
1.
Regular maintenance:
•
Ensure that your septic tank is
pumped and cleaned on a regular basis to prevent the buildup of solids and
avoid a foul odor.
•
Regularly inspect the system
for any leaks or cracks that may allow odors to escape.
1.
Use bacterial additives:
•
These additives can be
introduced into your septic system to promote the growth of beneficial
bacteria, which help break down waste and eliminate odors.
•
Choose additives that are
specifically designed for septic systems to ensure effectiveness.
Environmental
Benefits of Mound Septic Systems
Mound
septic systems provide you with the environmental benefits of efficient waste
treatment and reduced contamination risks. These systems are designed to
overcome challenging soil conditions or high water tables that can hinder the
proper functioning of traditional septic systems.
By
raising the drain field above ground level, mound septic systems create a mound
of specially engineered soil layers. This mound acts as a filter, allowing the
effluent to pass through and undergo further treatment before it reaches the
groundwater.
The
soil layers in the mound provide an aerobic environment where beneficial
bacteria break down the organic matter in the wastewater, effectively treating
it. This process helps to remove harmful pathogens and nutrients, reducing the
risk of contamination in nearby water sources.
Additionally,
mound septic systems often incorporate measures such as effluent pumps and
alarms to ensure proper functioning and minimize the potential for
environmental harm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the
Advantages of Using a Mound Septic System Over Other Types of Septic Systems?
Using a mound septic system offers several advantages over other
types of septic systems. It helps to treat waste effectively in areas with high
water tables or poor soil conditions, ensuring proper drainage and preventing
groundwater contamination.
How Long Does a
Mound Septic System Typically Last Before It Needs to Be Replaced?
A mound septic system typically lasts between 20-40 years before
needing replacement. This lifespan can vary depending on factors like
maintenance, usage, and environmental conditions. Regular inspections and
proper care can help prolong its longevity.
Can a Mound
Septic System Be Installed in Any Type of Soil?
Certainly! Mound septic systems can be installed in most soil types,
including clay, sand, and loam. However, the system's effectiveness may vary
depending on the soil's percolation rate and ability to properly filter and
treat the wastewater.
Are Mound Septic
Systems More Expensive to Install and Maintain Compared to Other Types of
Septic Systems?
Mound septic systems can be more expensive to install and maintain
compared to other types. The elevated drain field and additional materials
required for proper waste treatment contribute to the higher cost.
Are There Any
Specific Regulations or Permits Required for Installing a Mound Septic System?
To install a mound septic system, you must adhere to specific
regulations and obtain necessary permits. These requirements ensure proper
installation and protect the environment. Failure to comply can result in
penalties and delays.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mechanics
of mound septic systems offer an efficient and reliable solution for waste
treatment in areas with challenging soil conditions or high water tables. By
raising the drain field above ground level, these systems ensure proper
treatment of effluent.
Through careful site
evaluation, construction, and maintenance, mound septic systems provide
homeowners with a sustainable and environmentally friendly waste treatment
option.
Remember, 'out of sight, out
of mind' doesn't apply to waste management - choose a mound septic system for
peace of mind.


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment