Understanding the Basics: How Do Septic Tanks Work?
 |
| How Do Septic Tanks Work |
Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of septic tanks?
Prepare to be amazed as we unravel the inner workings of this essential waste
management system.
From the tireless efforts of bacteria to the intricate process of
waste breakdown, this article will equip you with the knowledge to understand
how septic tanks work.
Get ready to embark on an enlightening journey into the world of
septic tank systems and make informed decisions about their maintenance and
care.
Let's get started!
Key Takeaways
•
Septic tanks are used to safely
and efficiently treat and dispose of household waste by separating solid waste
from liquid waste.
•
Bacteria play a crucial role in
the decomposition process in septic tanks, with anaerobic bacteria breaking
down complex organic compounds and aerobic bacteria further breaking down
organic matter in the drainfield.
•
Regular removal of sludge and
scum is necessary to prevent clogging and system failure, and regular
maintenance and inspection are required to ensure proper functioning and avoid
costly repairs.
•
Following system maintenance
tips, such as scheduling regular inspections, pumping the septic tank every 3-5
years, avoiding flushing non-biodegradable items and excessive grease or oil,
and conserving water, can help ensure the longevity and efficiency of septic
tank systems.
The Purpose of Septic Tanks
Septic tanks
are designed to safely and efficiently treat and dispose of the waste generated
by your household. A septic tank system consists of a large underground tank
that's typically made of concrete or fiberglass. The main purpose of the septic
tank is to separate solid waste from the liquid waste.
When
wastewater flows into the septic tank, the solid waste settles at the bottom,
forming a layer of sludge, while the lighter materials, such as oils and fats,
float to the top, forming a layer of scum. Bacteria in the septic tank work to
break down the solid waste, converting it into liquid and gases.
The liquid
waste then flows out of the septic tank into the drain field, where it's
further treated and disposed of. Overall, septic tanks play a crucial role in
maintaining a healthy and functional septic system. They are often the only way in Rural Areas
The Components of
a Septic Tank System
The
components of a septic tank system include:
•
The septic tank itself: This is
a large underground container where the wastewater from your home is stored and
undergoes a natural decomposition process.
•
The drainfield, also known as the leach field: This is an area of soil where the treated wastewater is
dispersed and filtered before it reenters the groundwater.
•
The pipes that connect the
septic tank to the drainfield: These pipes transport the wastewater from the
septic tank to the drainfield for filtration and dispersal.
Having
these components working together is essential for the proper functioning of a
septic tank system. Proper maintenance and regular inspection are necessary to
ensure the system works efficiently and to prevent any issues that could lead
to costly repairs.
Bacteria and Decomposition
You might be
surprised to learn that bacteria play a crucial role in the decomposition
process within septic tanks. These microorganisms are responsible for breaking
down the organic matter present in the wastewater, allowing for the efficient treatment and disposal of sewage.
Here's how the
process works:
•
Bacterial Action:
•
Anaerobic bacteria: These
bacteria thrive in the oxygen-deprived environment of septic tanks. They break
down complex organic compounds into simpler substances such as carbon dioxide,
methane, and water.
•
Aerobic bacteria: Once the
partially treated wastewater leaves the septic tank and enters the drain field,
aerobic bacteria take over. They further break down the remaining organic
matter and remove any potential contaminants.
•
Decomposition Process:
•
Solid waste: Bacteria in septic
tanks decompose solid waste into sludge, which settles at the bottom, and scum,
which floats on top.
•
Liquid waste: The liquid waste,
or effluent, flows out of the septic tank and into the drain field, where it undergoes
further treatment through microbial action and soil filtration.
Understanding
how bacteria facilitate the decomposition process within septic tanks is
essential for maintaining proper functioning and preventing issues such as
clogging and system failure.
Sludge and Scum Removal
To prevent
clogging and system failure, regularly removing sludge and scum from your
septic tank is necessary. Sludge and scum are byproducts of the waste breakdown
process that occurs within your septic tank. Over time, these substances
accumulate and can cause blockages, leading to costly repairs or even the need
for a full tank replacement.
Sludge refers to
the solid waste that sinks to the bottom of the tank. It's made up of
undigested organic matter, such as food particles and toilet paper. Scum, on
the other hand, is the lighter waste material that floats to the top. It
consists of fats, oils, and grease.
Removing sludge
and scum is crucial to maintaining the proper functioning of your septic
system. Regular pumping and cleaning of the tank will help prevent the
accumulation of these substances, ensuring that your system operates
efficiently and avoiding potential issues down the line.
It's recommended
to have your septic tank pumped every 3-5 years, depending on the size of your
household and usage. By following this maintenance schedule, you can help
prolong the lifespan of your septic tank and avoid costly repairs or
replacements.
System Maintenance Tips
Regularly
maintaining your septic system is essential for preventing issues and ensuring
its long-term functionality. Here are some important maintenance tips to keep
your system running smoothly:
•
Schedule regular inspections: A
professional inspection every 1-3 years can help identify any potential
problems or signs of failure.
•
Pump your tank regularly:
Depending on the size of your tank and the number of occupants in your
household, pumping every 3-5 years is typically recommended.
•
Be mindful of what goes down
the drain: Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, chemicals, and excessive
amounts of grease or oil.
•
Conserve water: Excessive water
usage can overload your septic system, so be conscious of your water
consumption.
•
Protect your drain field: Avoid
parking vehicles or placing heavy objects on your drain field to prevent
damage.
The Role of
Bacteria in Septic Tank Functioning
Bacteria
play a vital role in the functioning of septic tanks by breaking down organic
waste materials. When wastewater enters the septic tank, it undergoes a process
known as anaerobic digestion.
This
process occurs in the absence of oxygen and is facilitated by the presence of
bacteria. These bacteria, known as anaerobic bacteria, break down the organic
solids in the wastewater, transforming them into simpler compounds such as
carbon dioxide, methane, and water.
This
breakdown of organic waste helps to reduce the volume of solids in the tank,
preventing it from overflowing or clogging the drain field. The effectiveness
of the septic tank relies heavily on the presence and activity of these
bacteria, making regular maintenance and the use of bacterial additives
essential for optimal functioning.
The Process of
Waste Breakdown in Septic Tanks
When
waste enters the septic tank, bacteria start their work of breaking down the
organic matter. These bacteria, known as anaerobic bacteria, thrive in the
oxygen-deprived environment of the tank. They convert the solid waste into
gases, liquids, and a layer of sludge at the bottom, while the lighter
particles form a layer of scum on top.
This
breakdown process is essential for the effective functioning of the septic tank
and the prevention of clogs or backups.
Bacteria's Role in Breakdown
You might be
wondering how exactly the bacteria in your septic tank contribute to the
breakdown of waste. Well, let's dive into the fascinating world of bacterial
activity in septic tanks. Here's how these tiny organisms work their magic:
•
Beneficial bacteria play a
crucial role in the breakdown of organic matter, such as human waste and food
particles, within the septic tank.
•
They break down complex
proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into simpler compounds through a process
called enzymatic digestion.
•
This process releases gases
like carbon dioxide and methane, which are then vented out of the tank.
•
The bacteria also help in
breaking down solids into liquid form, known as sludge, which settles at the
bottom, while lighter substances called scum float to the top.
•
The remaining liquid, known as
effluent, flows out of the tank and into the drain field for further treatment.
Function of Sludge/Scum
The sludge settles
at the bottom of the tank, while the scum floats to the top, helping to
separate and further breakdown waste. This separation process is a crucial step
in the functioning of septic tanks.
The sludge, which
is composed of heavier solids, such as organic matter and inorganic particles,
settles due to gravity. This layer of sludge accumulates over time and needs to
be regularly pumped out to prevent overflow and maintain the efficiency of the
tank.
On the other hand,
the scum, which consists of lighter substances like oils, fats, and grease,
forms a layer on top, preventing these materials from entering the drain field.
Together, the
sludge and scum play a vital role in the breakdown and filtration of waste
within the septic tank system.
Understanding
Sludge Accumulation in Septic Tanks
To
understand how septic tanks work, it's important to recognize the role of
bacteria in breaking down waste and the accumulation of sludge. Here's what you
need to know:
•
Bacteria play a crucial role in
the decomposition of organic matter in septic tanks. These bacteria feed on the
waste and convert it into simpler compounds.
•
The breakdown of waste by
bacteria produces gases, such as methane and carbon dioxide, which are released
into the atmosphere.
•
Sludge is the solid waste that
settles at the bottom of the septic tank. Over time, sludge accumulates and
needs to be pumped out periodically to prevent tank overflow.
•
Sludge accumulation can lead to
clogged pipes and reduced tank capacity, affecting the proper functioning of
the septic system.
•
Regular maintenance, including
sludge removal, is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your
septic tank.
The Significance
of Scum Layers in Septic Tanks
Don't
overlook the importance of scum layers in your septic tank, as they help
prevent excess grease and oils from entering the drainfield.
Scum
layers consist of a mixture of fats, oils, and other organic matter that float
on the surface of the wastewater in the tank.
These
layers play a crucial role in the functioning of the septic system by acting as
a barrier, preventing the passage of solids and preventing clogging of the
drainfield.
The
scum layer also helps in the natural breakdown of waste by providing an ideal
environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
These
bacteria consume the organic matter in the scum layer, breaking it down into
smaller, more manageable components.
Regular
maintenance, including periodic pumping of the septic tank, is essential to
ensure that the scum layer remains effective in its function.
Maintaining and
Troubleshooting Septic Tank Systems
You
can easily troubleshoot and maintain your septic tank system by regularly
inspecting for leaks and ensuring proper drainage. Here are some key steps to
follow:
•
Inspect the tank for any signs
of leakage, such as wet spots or foul odors.
•
Check the drain field regularly
to ensure it isn't saturated or clogged.
•
Pump your septic tank every 3-5
years to remove accumulated solids and prevent clogs.
•
Avoid flushing
non-biodegradable items, such as wipes or feminine hygiene products, down the
toilet.
•
Be mindful of water usage to
prevent overloading the system.
•
Avoid planting trees or shrubs
with deep roots near the septic tank or drain field.
By
following these maintenance tips, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency
of your septic tank system.
Regular
inspections and proper care will help you avoid costly repairs and keep your
system functioning smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the
Potential Health Risks Associated With a Malfunctioning Septic Tank System?
What potential health risks are associated with a malfunctioning
septic tank system? When a septic tank malfunctions, untreated sewage can
contaminate groundwater and surface water, leading to the spread of harmful
bacteria and diseases.
Can Septic Tanks
Be Used in All Types of Soil?
Yes, septic tanks can be used in various types of soil. They are
designed to treat wastewater and separate solids, allowing the liquid to be
absorbed by the soil. Proper soil conditions are important for effective septic
tank function.
How Often Should
a Septic Tank Be Pumped?
You should have your septic tank pumped every 3-5 years to prevent
buildup of sludge and scum. Regular maintenance is necessary to keep your
system working efficiently and avoid costly repairs.
Are There Any
Environmentally-Friendly Alternatives to Traditional Septic Tank Systems?
Yes, there are environmentally-friendly alternatives to traditionalseptic tank systems. These include aerobic treatment units, constructed
wetlands, and composting toilets. These options help reduce water pollution and
conserve water resources.
What Are Some
Common Signs of a Failing Septic Tank System?
Some common signs of a failing septic tank system include slow
drains, foul odors, sewage backups, and lush green patches of grass over the
drain field. Regular maintenance can help prevent these issues.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You've now
unlocked the secrets of septic tank systems, becoming a master of waste
management.
With your newfound knowledge,
you can confidently navigate the world of septic tanks, ensuring their smooth
operation and longevity.
Remember, the power lies in
your hands to maintain and troubleshoot these essential systems.
So go forth, armed with this
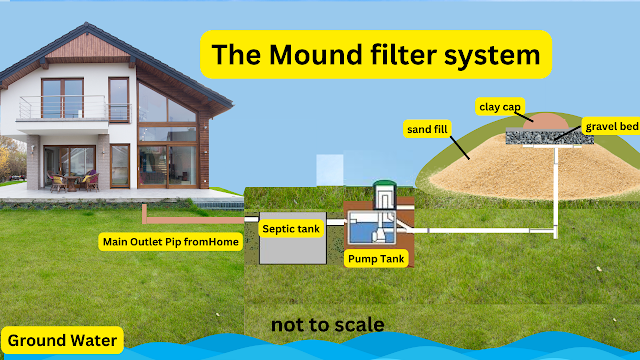
invaluable information, and conquer the world of septic tanks! Of course, they are other systems to explore like the Mound System


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment